Figure 2.
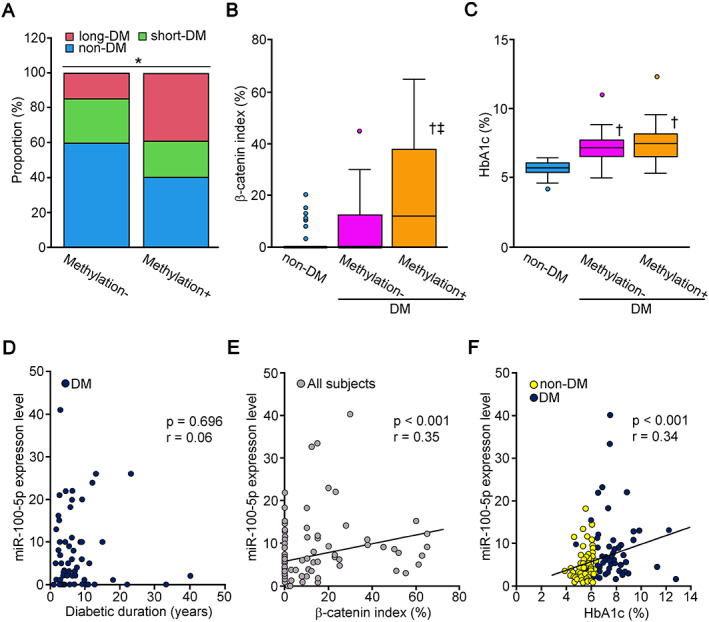
Correlation between epigenetic changes and diabetes‐related measurements. (A) The prevalence of a long duration of DM (≥3 years) was significantly higher in PDAC subjects with CDH1 promoter methylation than in PDAC subjects without CDH1 promoter methylation. (B) The β‐catenin index was significantly higher in DM subjects with CDH1 promoter methylation than in non‐DM subjects and DM subjects without CDH1 promoter methylation. (C) The HbA1c level was significantly higher in DM subjects than in non‐DM subjects regardless of the presence of CDH1 promoter methylation. The HbA1c level was comparable between the subjects with CDH1 promoter methylation − and +. (D) The duration of DM did not correlate significantly with the expression level of miR‐100‐5p (r = 0.06, p = 0.70). (E) The expression level of miR‐100‐5p was proportionally correlated with the β‐catenin index in all subjects (r = 0.35, p < 0.001). (F) The expression level of miR‐100‐5p was proportionally correlated with the HbA1c level in subjects with PDAC complicated with DM (r = 0.34, p < 0.001). Significance: *p < 0.05 (chi‐square test), † p < 0.01 versus non‐DM, ‡ p < 0.05 versus DM methylation−.
