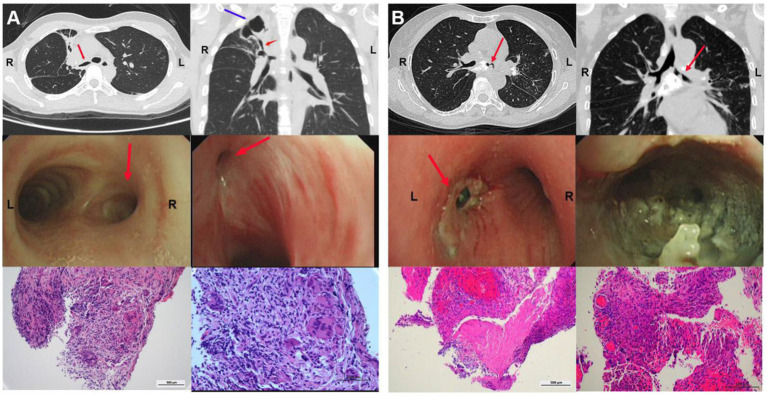
Figure 1.
Clinical characteristics of TBTS. (A) CT, bronchoscopy and pathology characteristics of a 39-year-old woman diagnosed with active TBTS. A CT scan revealed stenosis in right main and right upper bronchi, and a big tuberculous cavity was found in the right upper lobe. Mucosal swelling, granulation hyperplasia, lumen deformation and stenosis were observed with a bronchoscopy. Pathology showed that extensive granulation tissue hyperplasia and acid-fast bacilli and staining were positive, with inflammatory cell aggregation. (B) CT, bronchoscopy and pathology characteristics of a 23-year-old woman diagnosed with active TBTS. CT scan showed stenosis in the left main bronchus and the enlargement of mediastinal lymph nodes. A bronchoscopy demonstrated the obvious stenosis of the left main bronchus, a large amount of gray and white cheesy necrosis and visible bronchial lymph node fistula. H&E staining revealed cheesy necrosis and inflammatory cell aggregation. TBTS: tuberculous tracheobronchial stenosis.