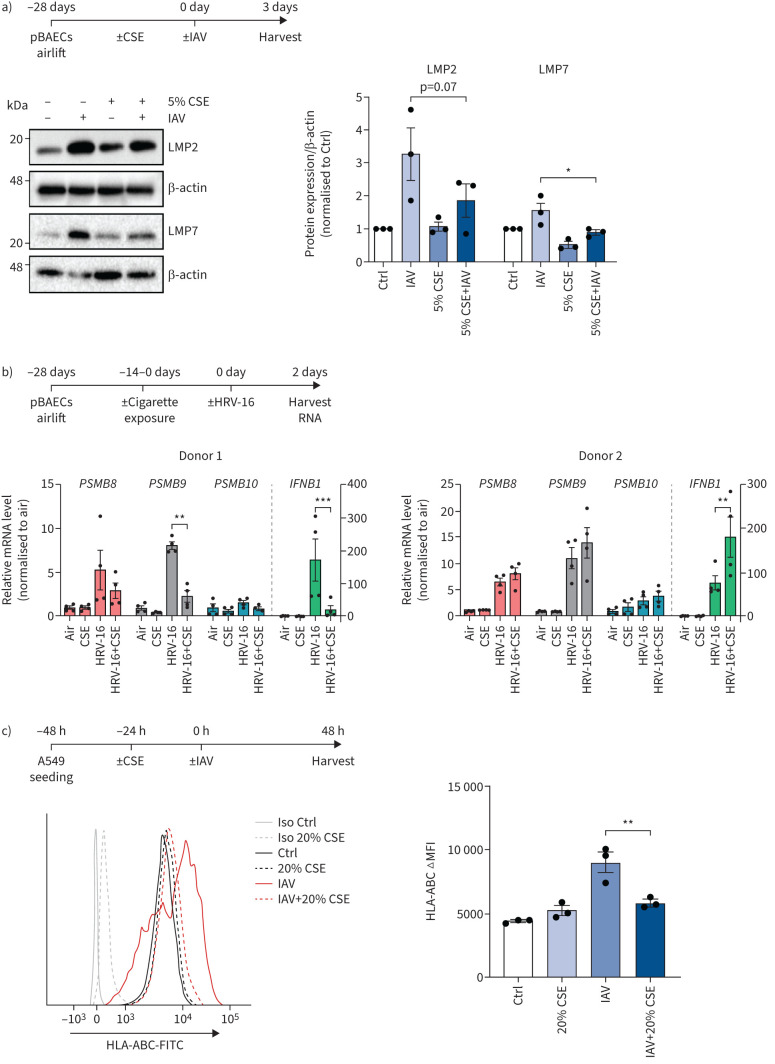
FIGURE 3.
Cigarette smoke impairs virus-mediated induction of the immunoproteasome and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I in human epithelial cells. a) Low molecular weight protein (LMP)2 and LMP7 expression in primary human bronchial epithelial cells (pBAECs) from three different donors that had been cultured at air–liquid interface conditions with or without cigarette smoke extract (CSE) in their medium [30] and infected with influenza A virus (IAV) for 3 days [60]. Densitometric analysis of LMP2 and LMP7 expression normalised to β-actin with untreated group set to 1. b) pBAECs from two male healthy donors were infected with human rhinovirus (HRV)-16 for 2 days after exposure to two cigarettes per day for 14 days during the air–liquid interface differentiation phase. mRNA levels for PSMB8 (LMP7), PSMB9 (LMP2) and PSMB10 (multicatalytic endopeptidase complex subunit (MECL)-1) and IFNB1 (interferon-β) were determined using reverse transcriptase quantitative PCR and related to housekeeping gene expression (HPRT and RPL32). Data are shown as four replicates per donor (mix of two technical and two independent cultures) with mean±sem. c) Human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-ABC surface expression of A549 cells treated with 20% CSE for 24 h and infected with IAV (multiplicity of infection 1) for 24 h. Fluorescence intensity is shown as mean±sem of three independent experiments. Ctrl: control; Iso: isotype; FITC: fluorescein isothiocyanate; ΔMFI: change in mean fluorescence intensity. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test. *: p<0.05, **: p<0.01, ***: p<0.001.