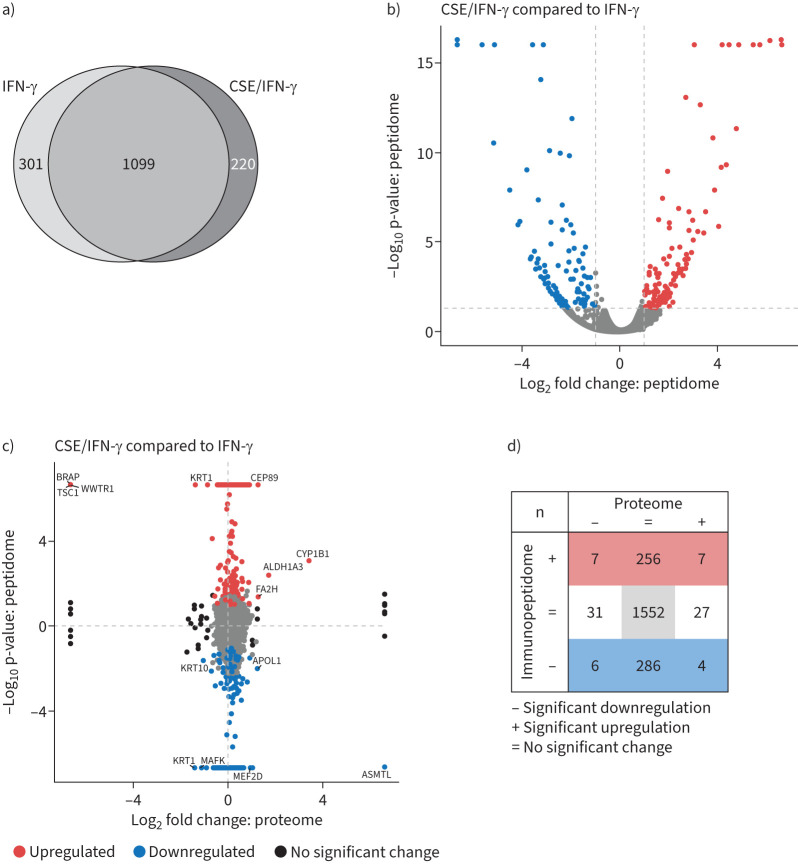
FIGURE 5.
Effect of cigarette smoke extract (CSE) on the inflammatory major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I immunopeptidome. a) Venn diagram of overlapping and unique MHC class I peptides identified in the immunopeptidome of A549 cells (binding rank ≤2%, confidence score ≥4.2, n=3). Cells had either been stimulated with 75 U·mL−1 interferon (IFN)-γ for 24 h or pre-treated with 20% CSE for 48 h and then co-stimulated with 75 U·mL−1 IFN-γ for the past 24 h. b) Volcano plot of the identified MHC class I peptides from a). Significantly upregulated peptides from CSE and IFN-γ-treated cells compared to IFN-γ treatment alone are depicted in red, significantly downregulated peptides are depicted in blue. A dashed horizontal line indicates the significance threshold of 0.05. The two dashed vertical lines indicate the log2 abundance ratio thresholds of −1 and 1. c) Abundance comparison of peptides identified in the immunopeptidome and proteins detected in the proteome from CSE and IFN-γ-treated cells compared to IFN-γ treatment alone. Significantly upregulated MHC class I peptides are depicted in red, while significantly downregulated MHC class I peptides are blue. Proteins significantly regulated in the proteome without significant changes in the peptidome are depicted in black. Peptides significantly regulated in the proteome and the immunopeptidome are labelled with their gene symbol. d) Enumeration of significantly regulated peptides from c).