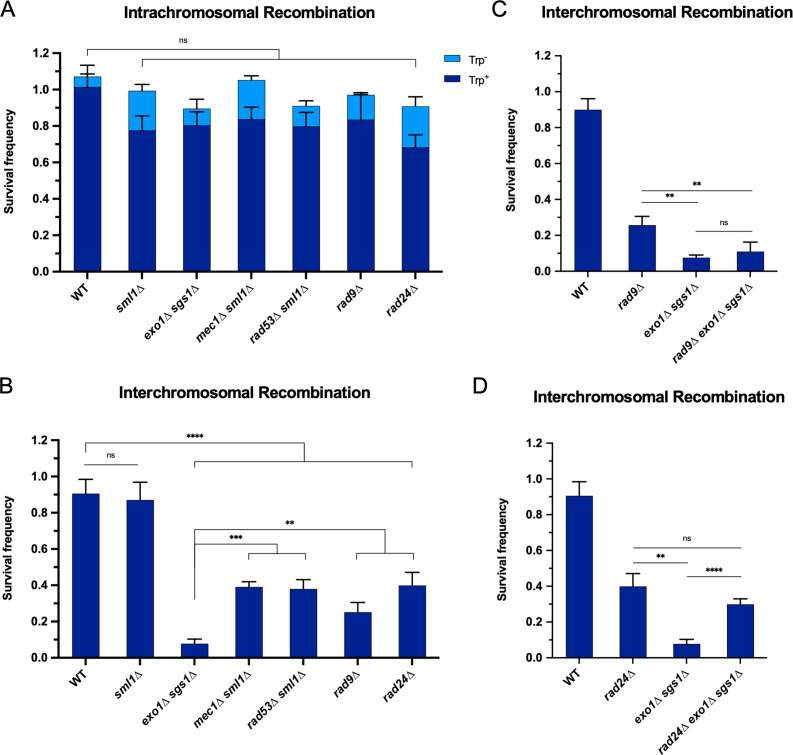
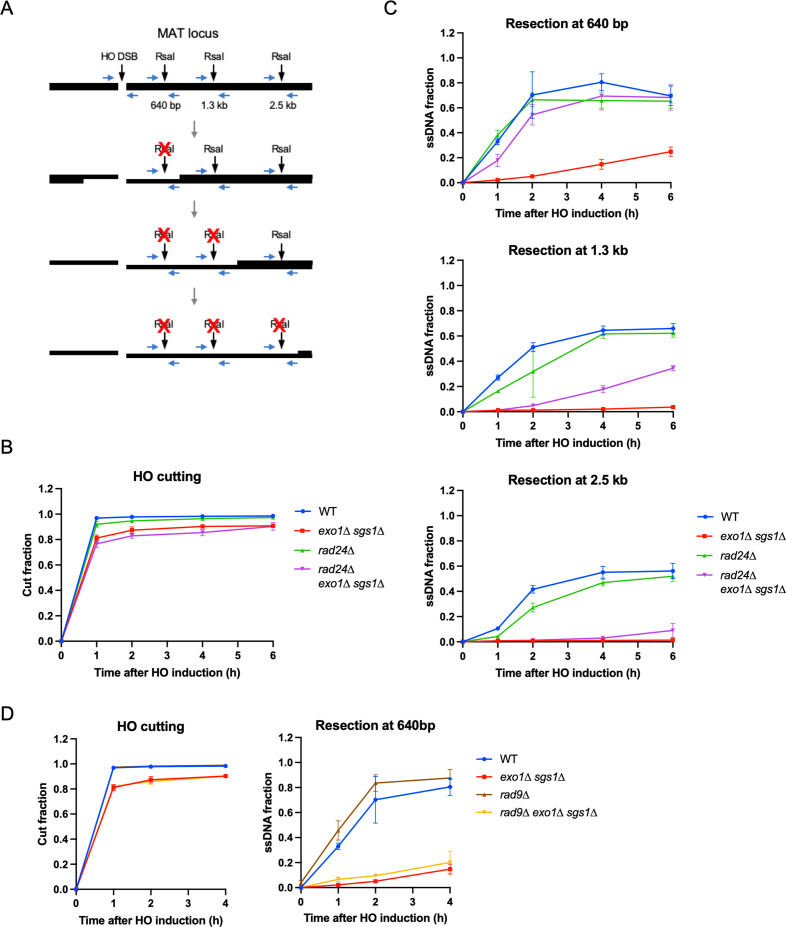
Figure 3. The requirement for long-range resection in interchromosomal recombination correlates with an increased requirement for the DNA damage checkpoint.
Survival frequency in the plating assay for the intrachromosomal strains (A) and interchromosomal strains (B–D) with the indicated genotypes. Intrachromosomal repair products are categorized as Trp+ or Trp-. Bars represent mean values from at least three plating assays per genotype. Error bars represent standard deviation. Significance values are indicated by: ns- not significant, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, **** p<0.0001 based on a two-tailed t-test. (C and D) contain overlapping data with B, so only relevant statistics are shown. Source data are available in Figure 3—source data 1.