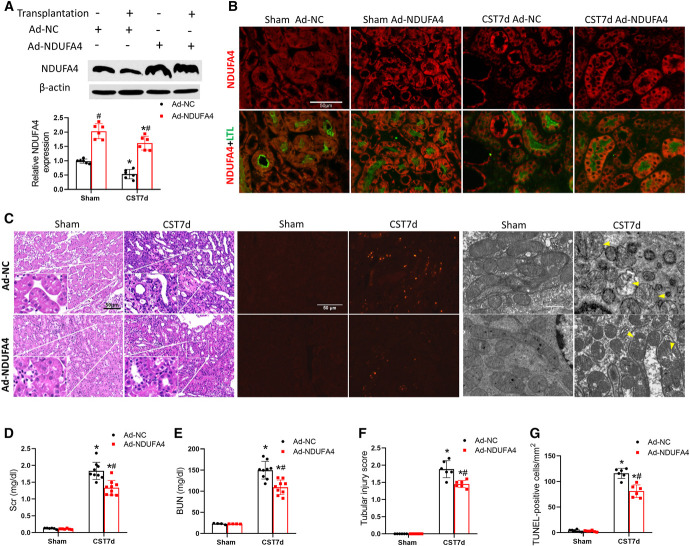
Figure 8.
NDUFA4 overexpression in the donor kidney ameliorates cold storage-associated transplantation injury. Donor mice kidneys were infected with Ad-NDUFA4 or Ad-NC, stored in cold for 10 hours, and then transplanted into recipient mice. On day 6 post-transplantation, the native kidney of the recipient mice was removed. On day 7, the transplanted kidney and blood samples were collected for analysis. The right kidney of donor mice without cold storage-associated transplantation was used as sham control. (A) Immunoblots verifying NDUFA4 overexpression following Ad-NDUFA4 infection. (B) Representative NDUFA4 immunofluorescence and LTL staining. (C) H&E staining of histology, TUNEL staining of apoptosis, and electronic microscopy images. Yellow arrowheads label swollen or damaged mitochondria. Scale bar=50 or 1 μm. (D) Serum creatinine. (E) BUN. (F) Pathological score of tubular damage. (G) Quantitative analysis of TUNEL-positive cells. Quantitative data are expressed as mean±SD (n=6–9), *P < 0.05 versus respective sham controls; #P < 0.05 versus Ad-NC–infected transplantation groups. Ad-NC, normal control adenoviral vector; Ad-NDUFA4, adenovirus containing NDUFA4; LTL, lotus tetragonolobus lectin; NC, negative control; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase–mediated digoxigenin-deoxyuridine nick-end labeling.