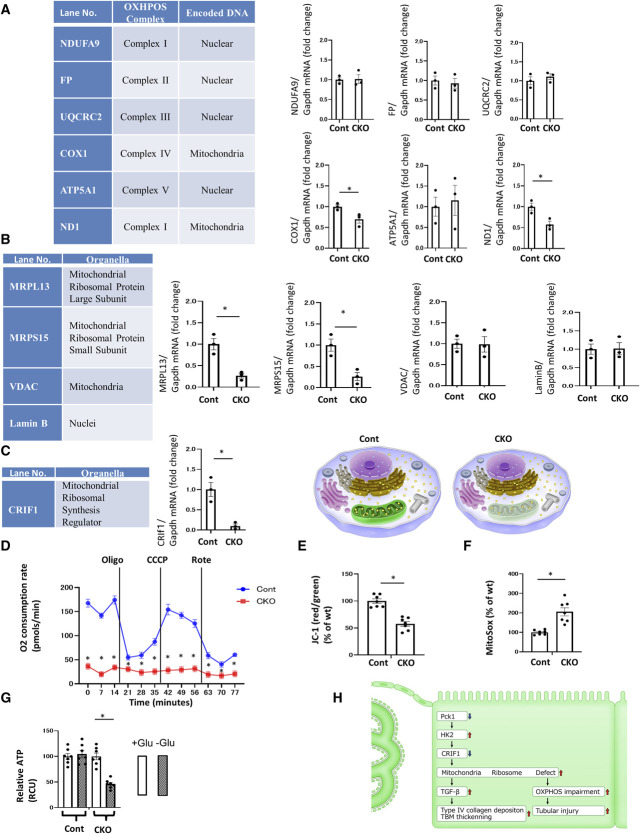
Figure 4.
The dysfunctional mitoribosomes and their concomitant mitochondrial dysfunction in CKO mice. (A) Real-time quantitative reverse transcription analysis of the renal mRNA levels of OXPHOS subunits encoded by nDNA and mtDNA. (B) Real-time quantitative reverse transcription analysis of renal mRNA levels of intracellular organelle markers. MRPL13 and MRPS15 are mitoribosomal proteins, whereas VDAC is a mitochondrial protein, and Lamin B is a nuclear protein. (C) Real-time quantitative reverse transcription analysis of the renal mRNA levels of CRIF1, a mitochondrial ribosomal synthesis regulator. Illustration depicting the dysfunctional mitoribosomes and their concomitant mitochondrial dysfunction in CKO mice. These functions are intact in control mice. (A–C) Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase was used as a control. The kidney tissue specimens for RT-PCR were obtained from CKO and control mice at age 32 weeks. N=3 mice per group. (D) OCR of TECs isolated from CKO and control mice was measured using a Seahorse XF-24 flux analyzer. N=3. (E) The ratio of red/green fluorescence of JC-1 of TECs isolated from CKO and control mice as a measure of mitochondrial membrane potential. N=7. (F) Fluorescence of MitoSox of TECs isolated from CKO and control mice as a measure of mitochondrial ROS levels. N=7. (G) ATP content of TECs isolated from CKO and control mice. N=7. All data are presented as mean±SEM. Horizontal bars indicate statistically significant differences between groups. *P < 0.05. (H) Scheme depicting the new mitoribosomes-mediated mechanism of renal profibrotic changes and tubular injury in CKO mice. The downregulation of Pck1 increased HK2 expression. Increased HK2 expression decreased the expression of CRIF1, causing mitoribosomal defects. The upregulation of mitoribosomal defects leads to the deposition of collagen IV in addition to the OXPHOS impairment and tubular injury.