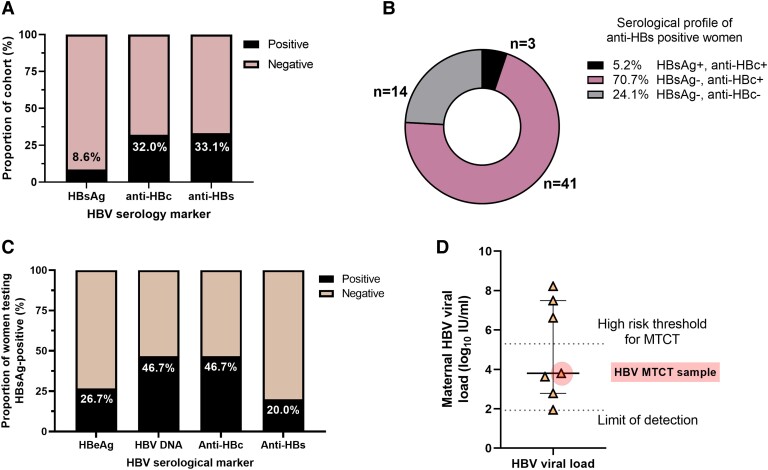
Figure 1.
A–D, HBV serologic profiles of mothers in a cohort of HIV MTCT pairs in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. A, All women in the cohort (N = 175) were tested for HBV surface antigen (HBsAg), HBV anti-core IgG (anti-HBc), and HBV anti-S (anti-HBs). B, Serological profiles of anti-HBs positive women (n = 58). HBV vaccination was likely in women with HBsAg–/anti-HBc– status, with the presence of any other HBV biomarker (HBsAg and/or anti-HBc) suggesting that immunity is the result of previous infection. C, Additional testing of women who were HBsAg positive is presented (n = 15), which included HBV e-antigen (HBeAg) and HBV DNA. D, Seven women who were HBsAg positive had HBV viral loads above the limit of detection (1.92 log10 IU/mL). The viral load of the maternal sample from the HBV MTCT pair is highlighted in red. The high-risk threshold for MTCT of HBV is also indicated (5.3 log10 IU/mL). Data are presented as median (IQR). HBV, hepatitis B virus; MTCT, mother-to-child transmission.