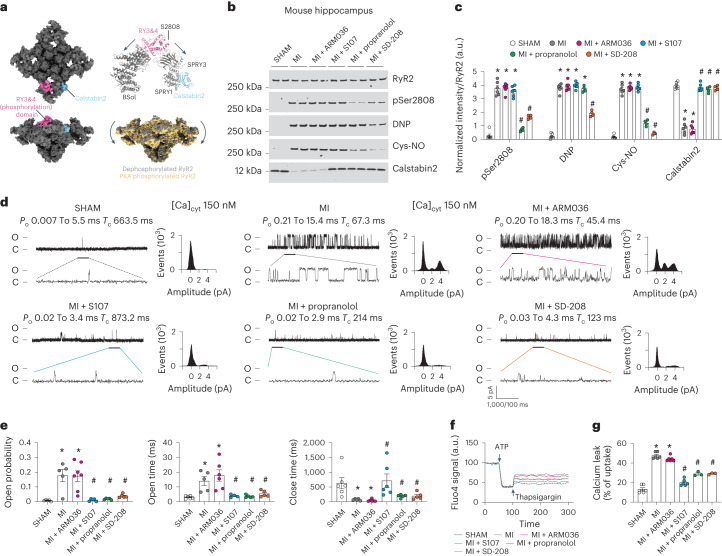
Fig. 3. Mouse model of heart failure is associated with leaky hippocampal RyR2.
a, Cryogenic electron microscopy structure of RyR2 (gray, top and side view) showing the location of the Ser2808 in the RY3&4 phosphorylation domain (magenta) and calstabin2 (cyan). RyR2 PKA phosphorylation shifted the channel toward a primed state (yellow)50. b,c, Representative SDS–PAGE analysis and quantification of modified RyR2 and calstabin2 immunoprecipitated from hippocampal RyR2 complex (IP RyR2; bands normalized to total RyR2) in SHAM (n = 6), MI (n = 6), MI + ARM036 (n = 6), MI + S107 (n = 6), MI+ propranolol (n = 4) and MI + SD-208 (n = 4) mice. d, Single-channel traces of RyR2 incorporated in planar lipid bilayers with 150 nM Ca2+ in the cis chamber, corresponding to representative experiments performed with hippocampal samples from SHAM (n = 6), MI (n = 5), MI + ARM036 (n = 6), MI + S107 (n = 5), MI + propranolol (n = 5) and MI + SD-208 (n = 5) mice. e, RyR2 Po, To and Tc in the same groups. f, Ca2+ leak measured in microsomes from mouse hippocampi of the same groups. g, Bar graphs represent the quantification of Ca2+ leak as the percentage of uptake in SHAM (n = 6), MI (n = 6), MI + ARM036 (n = 6), MI + S107 (n = 6), MI + propranolol (n = 3) and MI + SD-208 (n = 3) mice. Individual values are shown with the mean ± s.e.m. One-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test post hoc correction for multiple comparisons shows *P < 0.05, SHAM versus MI or MI + ARM036; #P < 0.05, MI versus MI + S107, MI + propranolol or MI + SD-208. Data are derived from biologically independent samples. All statistical tests were two sided.