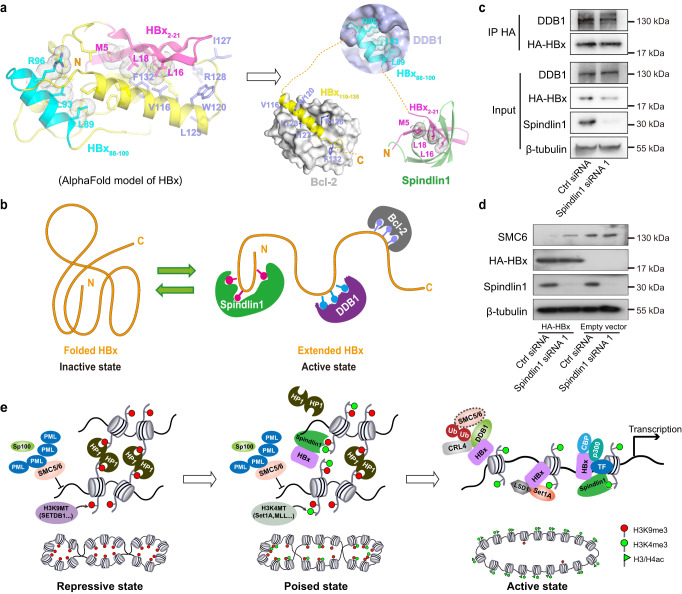
Fig. 7. Crosstalk between Spindlin1-HBx and DDB1-HBx engagements.
a AlphaFold model of free HBx (left) and structure model of HBx binding to Spindlin1 (light magenta-green), DDB1 (cyan-gray, PDB ID 3I7H), and Bcl-2 (yellow-white, PDB ID 5FCG). b Schematic model of HBx transitioning from an inactive state to an active one by binding to Spindlin1, DDB1, and Bcl-2. c Co-IP of HA-HBx with endogenous DDB1 using anti-HA antibodies in HepG2-NTCP cells, which were transfected with Ctrl siRNA or Spindlin1 siRNA 1. d WB analyzing the SMC6 level in Spindlin1 knockdown HepG2-NTCP cells expressing HBx. Cells were transfected with Ctrl siRNA or Spindlin1 siRNA 1 for 72 h and then transfected with HA-HBx or empty vector. After 96 h, cells were harvest for WB analyzation. (c–d) n = 3 independent experiments. e A schematic model of Spindlin1-HBx mediated transcriptional derepression of cccDNA minichromosome. Chromatinized HBV genome undergoes epigenetic reprogramming from a repressive state to an active state via a poised intermediate state. The transcriptionally inactive HBV genome is typically silenced by host restriction factors, such as PML, Sp100, SMC5/6, H3K9 methyltransferases (H3K9MT), and HP1, which form a repressive chromatin state marked by H3K9me3 (left). To overcome the heterochromatin barrier, histone H3K4 methyltransferases (H3K4MT) can target H3K9me3-containing cccDNA chromatin to create bivalent H3 “K4me3-K9me3” modifications49. Spindlin1-HBx complex then binds to H3 “K4me3-K9me3” and competes off HP1 from the poised state chromatin (middle). Finally, Spindlin1 and HBx cooperatively establish an active chromatin state of HBV cccDNA in concert with transcription factor (TF) and co-activators such as CBP/p300 to promote HBV transcription (right). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.