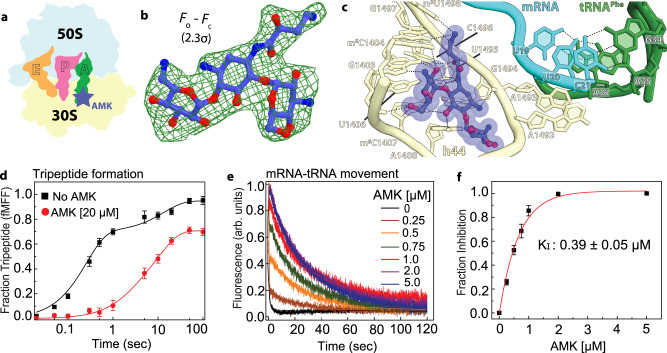
Fig. 2. Canonical binding site of amikacin near the decoding center.
a Simplified representation of the 70S ribosome with the AMK binding site indicated with the blue star. b The unbiased (Fo – Fc) difference electron density map of AMK bound near the decoding center is contoured at 2.3σ. c AMK binds within helix h44 of the decoding center where the AHB moiety forms three unique interactions. d Time courses of f[3H]Met-Phe-Phe tripeptide formation with EF-Tu ternary complex (TC) (5 μM) and EF-G (5 µM) in the absence (black) and presence of 20 μM AMK (red). Solid lines represent the double exponential fit of the data with SEM from n = 3 independent experiments. e Time evolution of fluorescence traces obtained for the EF-G (5 μM) catalyzed movement of pyrene-labeled mRNA on 70S ribosomes (0.5 μM) in the presence of various concentrations (0-5 µM) of AMK. The inhibition of mRNA movement by AMK was estimated from amplitudes of the slow phase of fluorescence traces relative to the total transition (normalized to 1) indicative of inhibited fraction of the ribosomes. f The fraction of AMK-inhibited pre-TC plotted against AMK concentration. Data were fitted with hyperbolic function (solid line) and half-inhibitory concentration (KI) of AMK on the inhibition of translocation was estimated from mid-point of transition. Experiments were conducted in triplicates and error bars indicate the SEM of data.