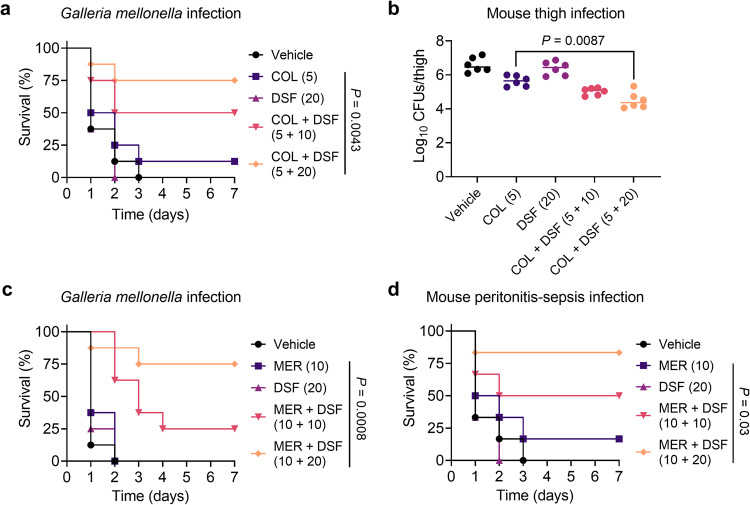
Fig. 7. DSF improves the in vivo efficacy of colistin and meropenem.
a Survival rates of the G. mellonella larvae (n = 8 biologically independent animals per group) infected by E. coli B2 (106 CFUs). Compared with colistin monotherapy (5 mg/kg), the combination therapy of colistin and DSF (5 + 20 mg/kg) significantly improved the survival rates of G. mellonella. b Bacterial loads of the CD-1 mice (n = 6 biologically independent animals per group) infected by E. coli B2 (105 CFUs). Compared with colistin alone, the combination therapy of colistin and DSF reduced bacterial loads of thigh muscle. P-values were determined by Mann-Whitney U test. c Survival rates of the G. mellonella larvae (n = 8 biologically independent animals per group) infected by E. coli C3 (106 CFUs). Compared with the meropenem monotherapy (10 mg/kg), the combination therapy of meropenem and DSF (10 + 20 mg/kg) significantly improved the survival rates of larvae. d Survival rates of the CD-1 mice (n = 6 biologically independent animals per group) infected by E. coli C3 (108 CFUs) and treated with a single dose of meropenem (10 mg/kg), DSF (20 mg/kg), a combination of meropenem plus DSF (10 + 10 mg/kg, 10 + 20 mg/kg), or PBS by intraperitoneal injection. In (a), (c) and (d), P values were determined by log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test.