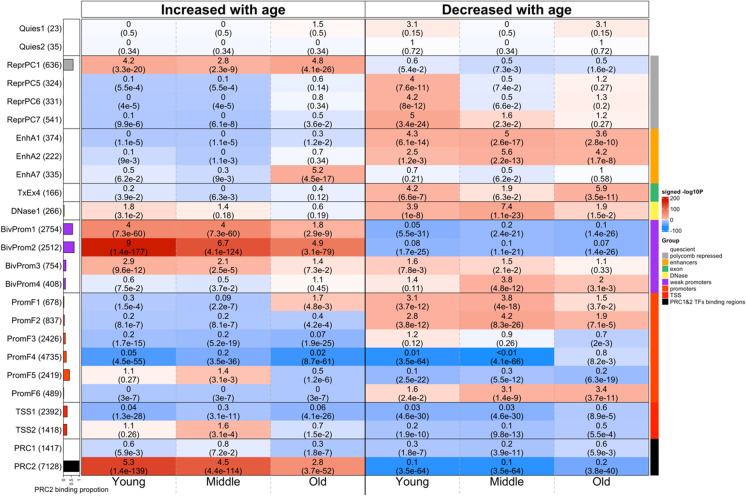
Fig. 4.
Chromatin state analysis of age-related CpGs. Chromatic state annotation and polycomb repressive complex (PRC) annotation for the age-related CpGs identified from EWAS of age in three age groups: (1) young for age between 0 and 40, (2) middle for age between 40 and 90, and (3) old for age between 90 and 115. The heatmap color codes the hypergeometric overlap analysis between age-related CpGs (columns) and (1) universal chromatin states analysis [33] and PRC1-/PRC2-binding sites defined based on ChipSeq data sets in ENCODE [34]. For each row, the table reports odds ratios (OR) from hypergeometric test results for the top 1000 CpGs that increased/decreased with age from our EWAS of age in three age groups (young, middle, old). The color gradient in the heatmap is based on − log10 (unadjusted hypergeometric P value) multiplied by the sign of OR greater than one. Red colors denote OR greater than one in contrast with blue colors for OR less than one. Legend lists states based on their group category. The y-axis lists the chromatin state or PRC binding and the respective number of CpGs inside parentheses. The bar plot on the left reports the proportion of CpGs that are known to be bound by PRC2 that ranges from zero (PRC1) to one (PRC2). The left/right panel lists the results based on the top 1000 CpGs with positive and the top 1000 CpGs with negative age correlations, respectively. We displayed 23 universal chromatin states that show significant enrichment/depletion at an uncorrected/nominal P < 1.0 × 10−10 in any of the EWAS