Figure 1.
Targeting and internalization of the α9-nAChR RNA aptamer in TNBC cells
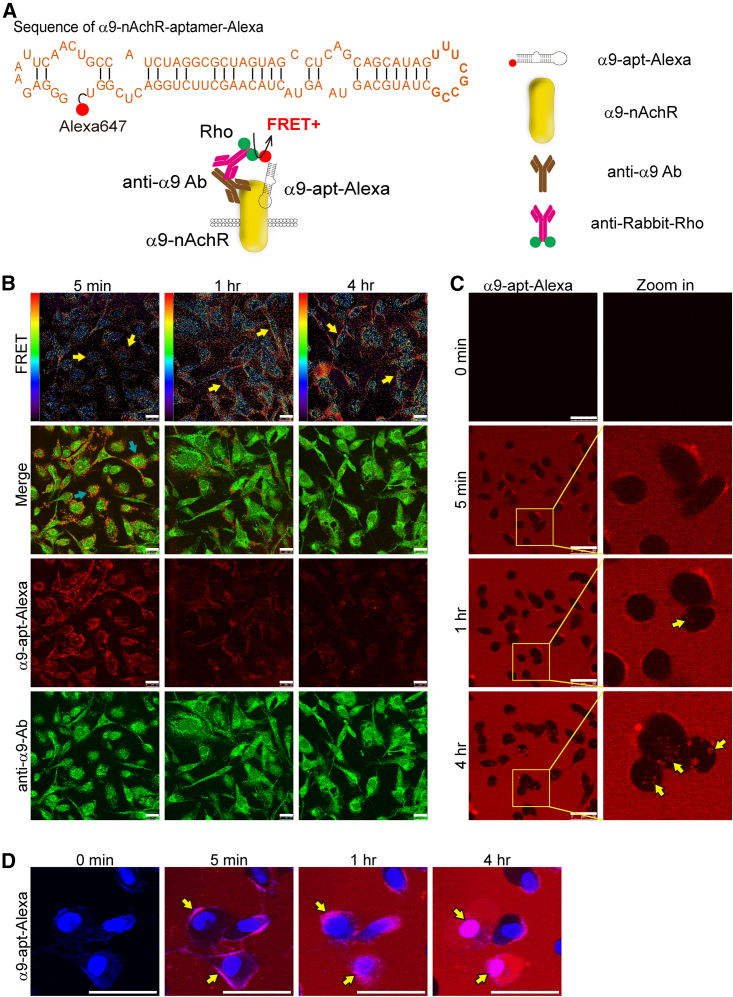
(A) The schematic shows the sequence of the α9-nAChR RNA aptamer labeled with Alexa 647 (top) and the fluorescent staining strategy for detecting the FRET signal between α9-nAChR and α9-apt-Alexa (bottom). The α9-nAChR proteins are detected using antibodies specific to α9nAchR and labeled by a secondary rabbit antibody with rhodamine (Rho; green dots). (B) Time-dependent fluorescence and FRET images in MDA-MB-231 cells after α9-apt-Alexa treatment. Scale bar, 25 μm. The red/blue spectrum represents the intensity of FRET efficiency. Yellow arrows indicate a positive FRET signal. (C and D) Time-lapse fluorescence live-cell images of MDA-MB-231 cells after α9-apt-Alexa treatment. Yellow arrows indicate internalization of α9-apt-Alexa. Hochest 33342 is a nuclear indicator (blue) (D). Scale bars, 50 μm (C and D).