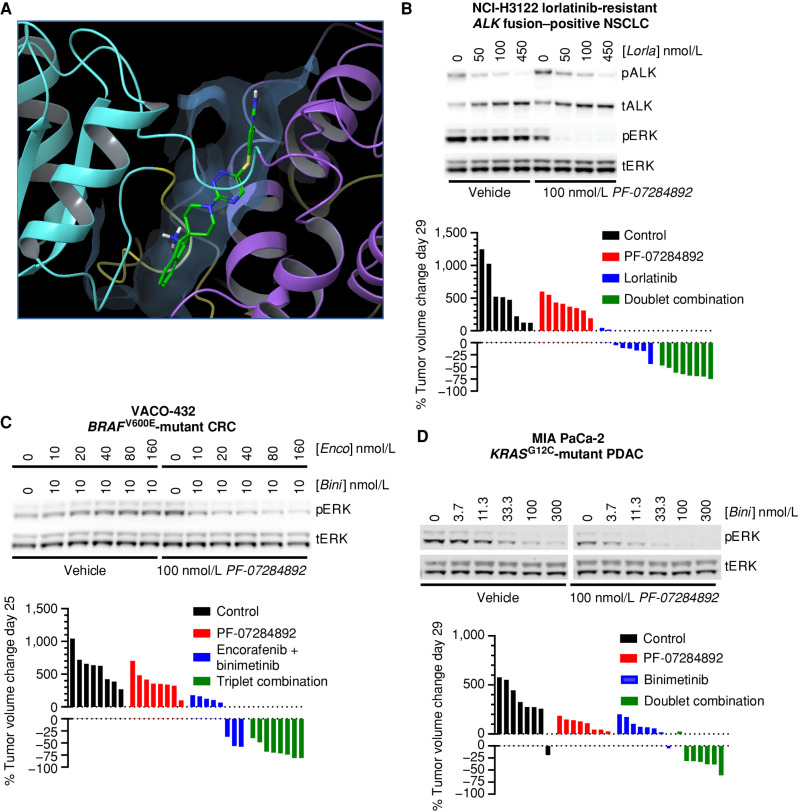
Figure 1.
PF-07284892 promotes antitumor efficacy in multiple oncogene-addicted models with up-front or acquired resistance to targeted therapies. A, X-ray crystal structure of PF-07284892–bound SHP2. N-SH2, C-SH2, and PTP domains are yellow, cyan, and violet; inhibitor is green/blue. See Supplementary Table S1 for data collection and refinement statistics. B–D, Top, the indicated human cancer cell lines were treated in vitro with each agent at the indicated concentrations for 4 (H3122 lorR-06), 18 (VACO-432), or 24 (MIA PaCa-2) hours followed by preparation of cell lysates and analysis of the indicated protein by immunoblot. Quantitation of each band is shown in Supplementary Fig. S3. Bottom, immunodeficient mice (8 per group) were xenografted subcutaneously with the same human tumor cells used for in vitro signaling analysis. When tumors reached ∼200 mm3, animals were treated orally with vehicle, PF-07284892 30 mg/kg q.o.d., lorlatinib 3 mg/kg qd, encorafenib 20 mg/kg qd + binimetinib 3.5 mg/kg b.i.d., binimetinib 3.5 mg/kg b.i.d., or with the indicated combinations (at the monotherapy doses). Tumor sizes on days 25 to 29 were normalized to day 1 prior to treatment. b.i.d., twice daily; Bini, binimetinib; C, carboxy-proximal; CRC, colorectal cancer; Enco, encorafenib; Lorla, lorlatinib; N, amino-proximal; NSCLC, non–small cell lung cancer; p, phosphorylated; PDAC, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; PTP, phosphatase; qd, daily; q.o.d., every other day; t, total.