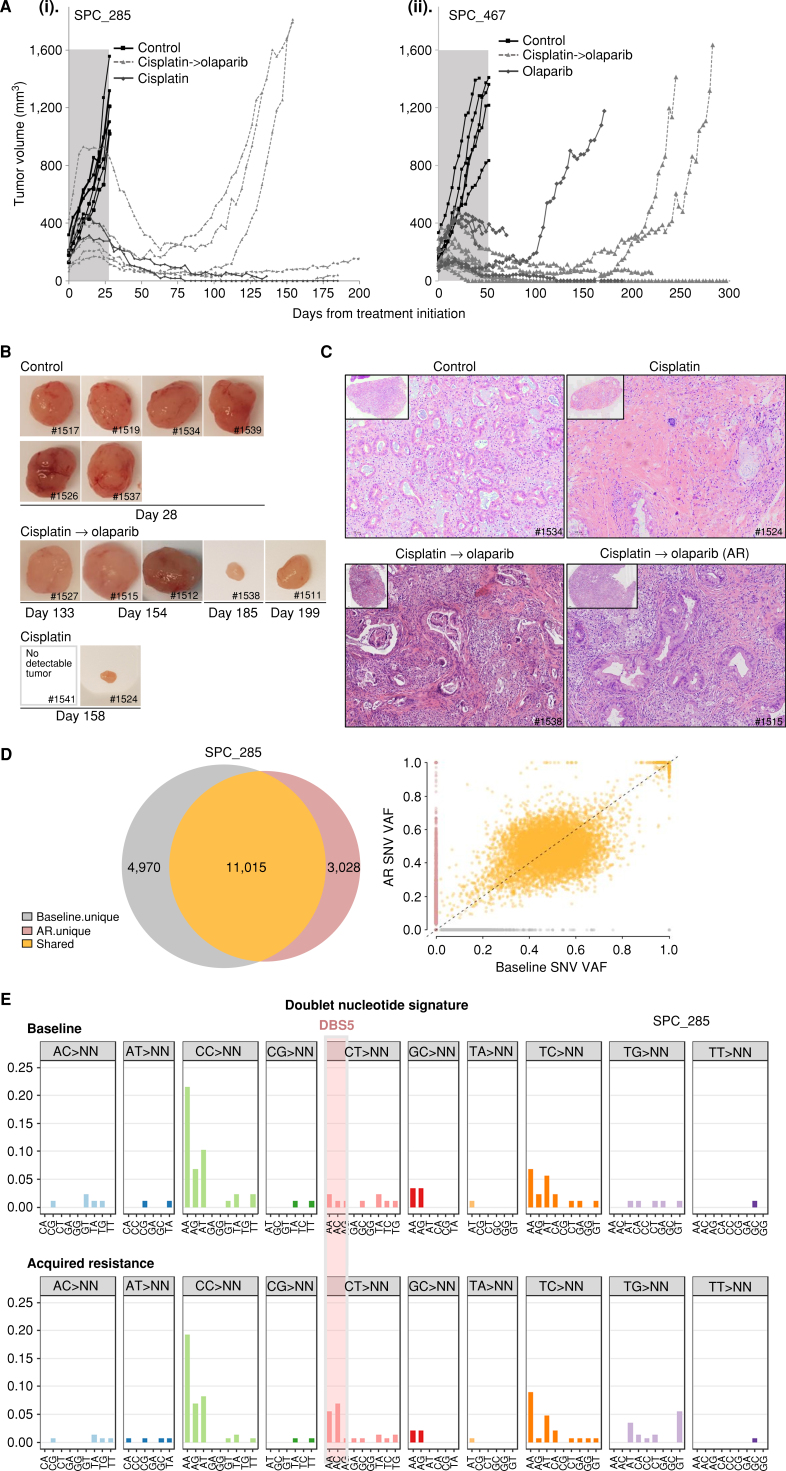
Figure 3.
Preclinical olaparib maintenance therapy and establishment of an in vivo acquired resistant model. A, Tumor growth kinetics of two BRCA2-mutated PDAC PDXs with biallelic inactivation. i, SPC_285: Mice were initially randomized to control (vehicle; i.p.; once weekly) or cisplatin (2 mg/kg; i.p.; once weekly); n = 6–7/group. Cisplatin was administrated for 28 days, and mice were then split to continue cisplatin (n = 2) or to switch to maintenance olaparib (50 mg/kg; i.p.; 5 days on/2 days off). ii, SPC_467: Mice were randomized to control (n = 7), olaparib (n = 5), or cisplatin (n = 13). On day 50, cisplatin-treated mice were switched to olaparib (50 mg/kg/i.p.; 5 days on/2 days off). B, Tumor images of SPC_285 for each treatment group (top, control; middle, cisplatin → olaparib; and bottom, cisplatin) on sacrifice day as indicated. C, H&E representative images of tumors treated in control, cisplatin, and cisplatin → olaparib groups. AR, acquired resistance. D, Top: Venn diagrams showing SNV overlap between platinum-sensitive baseline and AR samples. Scatter plots comparing single-nucleotide variant (SNV) variant allele frequencies (VAF) of AR xenograft samples to paired baseline. Bottom, dotted black line represents y = x, where SNV VAF of AR xenograft is equal to SNV VAF of the baseline. Baseline unique variants are shown in gray, whereas AR unique variants are in red and shared variants in orange. E, Double nucleotide alterations characterized by doublet base substitutions of CT>AA/AC in the acquired resistance exposed to the platinum/PARPi model.