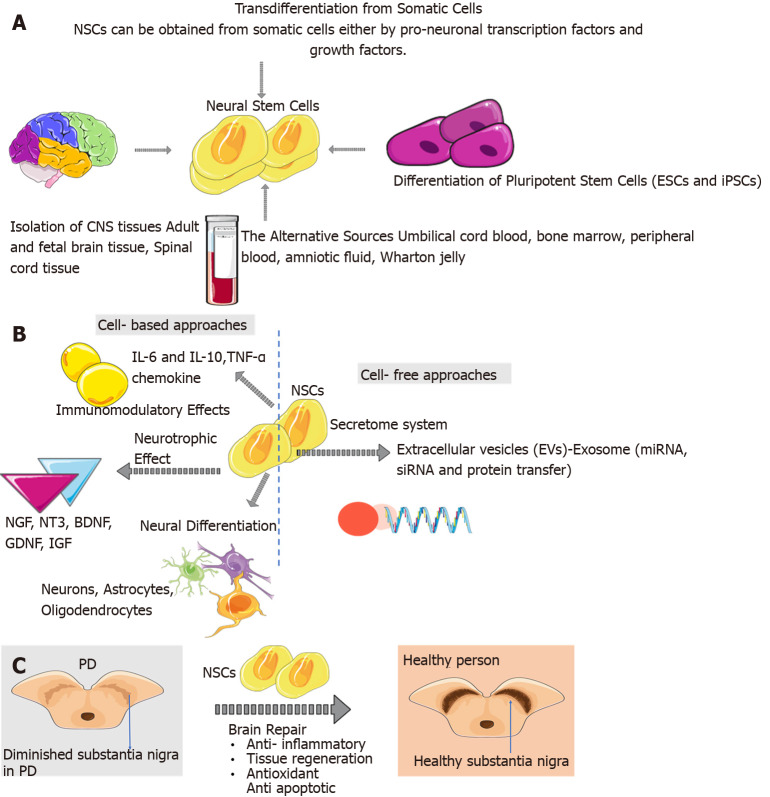
Figure 1.
Emergence of neural stem cells in the adult brain and alternative sources of neural stem cells. A: The sources of neural stem cells (NSCs) are embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells, adult/foetal brain tissue and spinal cord tissue. Also, NSCs can be obtained from somatic cells either by transcription factors and growth factors. The alternative sources of NSCs are foetal and adult nervous systems, umbilical cord blood, bone marrow, peripheral blood, amniotic fluid, Wharton jelly; B: NSCs can have immunomodulatory effects such as cytokine, chemokines, and chemokine receptors secretion and T cell proliferation inhibition. NSCs can have neurotrophic effects such as nerve growth factor, neurotrophin-3, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. NSCs can target secretome and paracrine effects via extracellular vesicles like exosomes. Also, NSCs play a role in neural differentiation; C: NSCs after their transplantation, could migrate, survive, and proliferate in specific brain sites. And NSCs play a role in brain repair mechanisms such as antiapoptotic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant. CNS: Central nervous system; BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; ESCs: Embryonic stem cells; EVs: Extracellular vesicles; GDNF: Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; iPSCs: Induced pluripotent stem cells; NGF: Nerve growth factor; NT-3: Neurotrophin-3; NSCs: Neural stem cells; TFs: Transcription factors; PD: Parkinson’s disease; TGF: Transforming growth factor. Citation: The parts of the figures were drawn using pictures from Servier Medical Art. Servier Medical Art by Servier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by/3.0/).