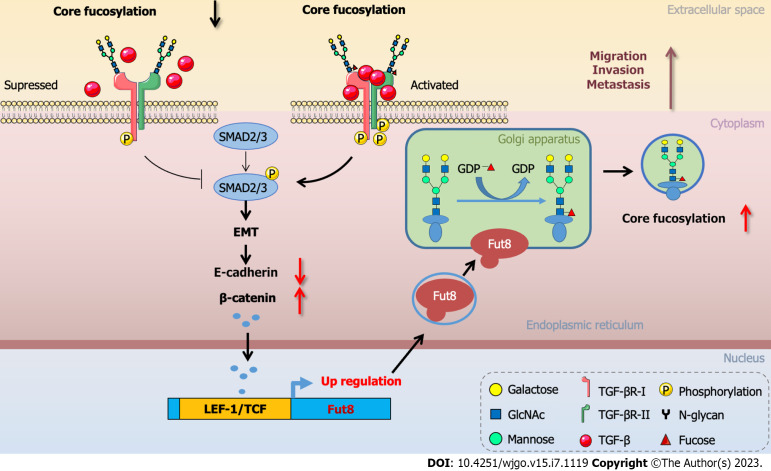
Figure 3.
Core fucosylation modulated epithelial to mesenchymal transition during cancer progression. Loss of core fucosylation impaired the binding of transforming growth factor β to its receptor and inhibited the phosphorylation of regulatory Smad2 and Smad3. During epithelial to mesenchymal transition, the expression of E-cadherin was suppressed, resulting in the accumulation of β-catenin in the nucleus, where it complexed with lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 to transactivate fucosyltransferase 8 expression. The core fucosylation level on surface molecules of cancer cells was increased which promoted cancer cell malignant biological properties involving migration, invasion, and metastasis. EMT: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition; TCF: T cell factor; LEF: Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1; TGF: Transforming growth factor. This figure was summarized and modified from Tu et al[46], Chen et al[74], and Lin et al[101].