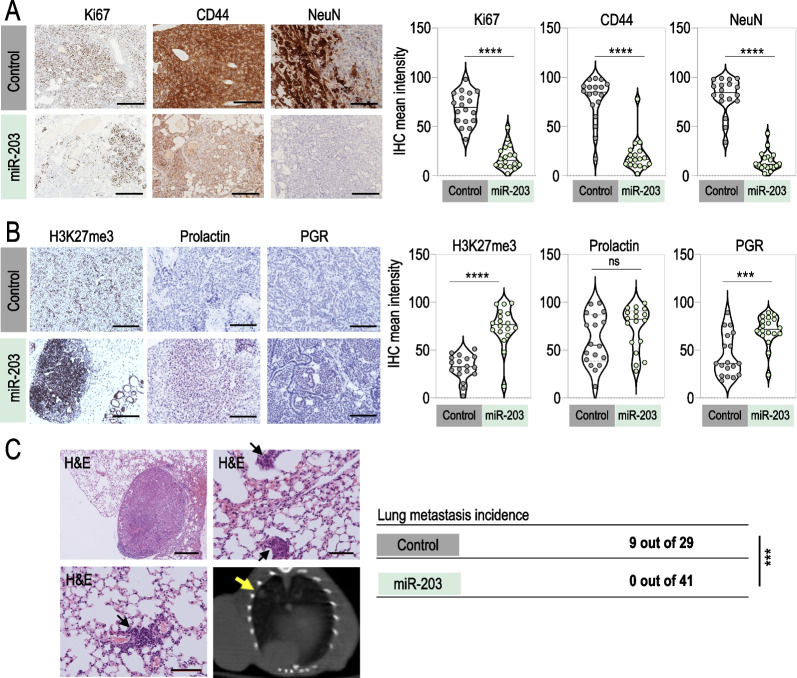
Fig. 4.
miR-203 exposure in vivo on PyMT mice alters the expression of stem-like and differentiation markers in mammary tumors and fully prevents lung metastasis. A Left panel, Representative images of IHC staining for Ki67 (to test proliferation), CD44 and NeuN (as stem-like cell markers) in control and miR-203-treated tumors, at the experimental endpoint and after exposure to Dox on alternating weeks from tumor detection by micro-CT, as indicated in Fig. 3A. Right panel, Violin plots showing the quantification of markers staining. B Left panel, Representative images of IHC staining for H3K27me3, prolactin and progesterone receptor (PGR), to test evidences of differentiation on control and miR-203-treated tumors as in (A). Right panel, Violin plots showing the quantification of markers staining. C Illustrative H&E staining of lung macro- and micro-metastasis, found in several control mice at the experimental human endpoint. Representative examples are shown, from the 9 metastasis cases identified throughout the three in vivo experiments (depicted in Figs. 1, 2, 3). As shown in the table, the overall incidence of metastasis was 31,03% in control mice versus 0% in miR-203-treated mice. The bottom right panel shows a representative micro-CT image, pointing to one evident macro-metastasis (yellow arrow) found in a control mouse. Scale bar, 500 µm. In violin plots, six different fields from three independent tumor samples were analyzed. ****p < 0.0001; ***p < 0.001; n.s. not statistically different (Student’s t test)