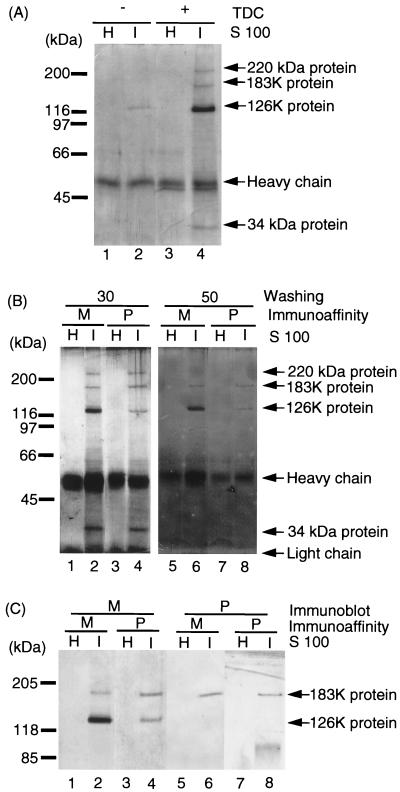
FIG. 1.
Immunoaffinity purification of the 126K and 183K proteins with anti-M and anti-P antibodies. (A) Immunoprecipitation of the 126K and 183K proteins from TDC-treated extracts of TMV-infected tobacco. By starting with 1.25 g of TMV-infected or uninfected tobacco leaves, 250 μl of S100 was obtained in the presence (+) or absence (−) of TDC. The S100 fractions were incubated with anti-M antibody-Sepharose. After a washing with 30 bed volumes of Tris-Triton-NaCl buffer, proteins were eluted from the immunoaffinity resins and subjected to SDS–7.5% PAGE. Proteins in the gel were detected by silver staining. H, uninfected healthy tobacco leaves; I, TMV-infected tobacco leaves. The major protein bands detected are shown on the right, i.e., the 183K and 126K TMV proteins and the 220- and 34-kDa host proteins (see text). The migration positions of the molecular-weight markers are shown on the left. (B) Immunoaffinity purification of the 126K and 183K proteins with anti-M and anti-P antibodies. TDC-treated S100 fractions of TMV-infected and uninfected healthy tobacco leaves were incubated with either anti-M or anti-P antibody-Sepharose. The antigen-bound antibody-Sepharose was washed with 30 (lanes 1 to 4) or 50 (lanes 5 to 8) bed volumes of the Tris-Triton-NaCl buffer. Eluates from these immunoaffinity Sepharose resins were subjected to SDS–7.5% PAGE, and proteins were detected by silver staining. M, anti-M antibody-Sepharose; P, anti-P antibody-Sepharose; H, healthy tobacco leaves; I, TMV-infected tobacco leaves. The proteins identified are indicated on the right, i.e., the 183K and 126K TMV proteins and the 220- and 34-kDa putative host proteins. The migration positions of the molecular-weight markers are shown on the left. (C) Identification of the 126K and 183K proteins in the immunoaffinity-purified RNA polymerase. S100 fractions prepared from healthy tobacco leaves (H) and TMV-infected tobacco leaves (I) were subjected to immunoaffinity purification of the 126K and 183K proteins by using anti-M (M) or anti-P (P) antibody-conjugated Sepharose. After a washing with 50 bed volumes of Tris-Triton-NaCl buffer, the eluates from the immunoaffinity columns were subjected to SDS–7.5% PAGE, and the proteins were detected by immunostaining with polyclonal antibodies against M (lanes 1 to 4) or P (lanes 5 to 8). The positions of the molecular-weight markers are shown on left.