Fig. 2.
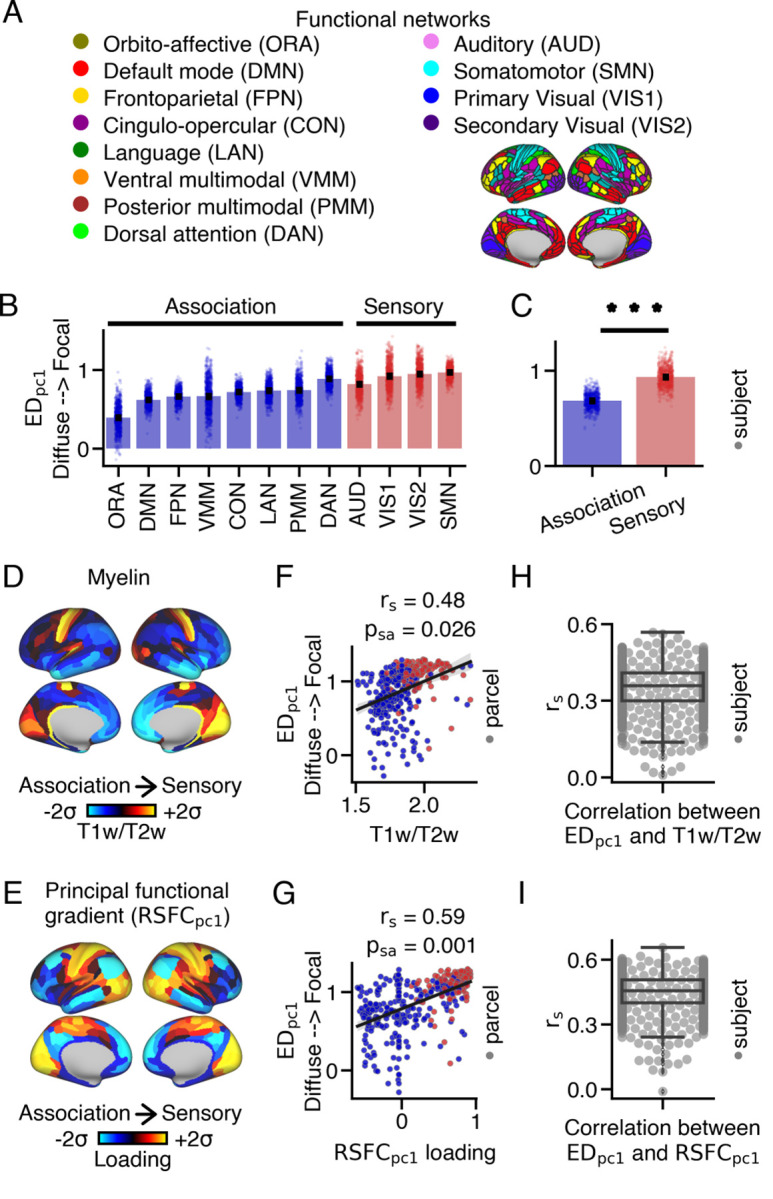
Differences in the extent of anatomical connections within the thalamus between sensory and association cortical parcels. (A) Resting-state functional connectivity networks identified by Ji et al. (48). (B) Average loading within each network for each subject. Barplots show the mean and standard error. (C) Sensory networks exhibited significantly higher loadings compared to association networks (two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank test; ). (D) Cortical myelin map calculated by averaging T1w/T2w values across subjects. (E) Cortical principal functional gradient () loading map derived from PCA on cortico-cortical resting-state functional connectivity data. Sensory cortical parcels exhibit higher T1w/T2w values and loadings compared to association cortical parcels. (F,G) Correlations between loadings and T1w/T2w values, as well as loadings, across the cortex. (H,I) On average, a moderate relationship was observed between loadings and T1w/T2w values, as well as loadings, across subjects. Boxplots show the median and inter-quartile ranges.
