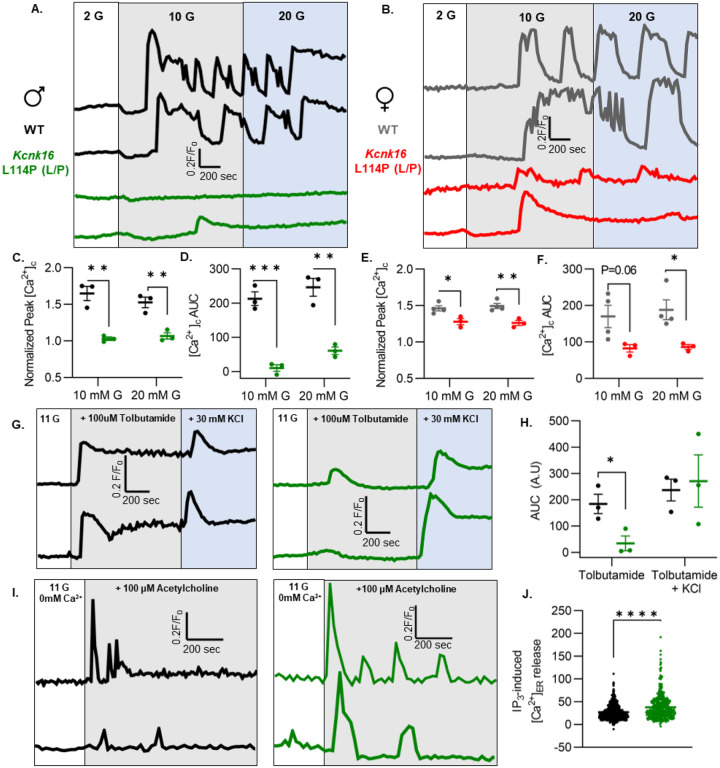
Figure 5. Kcnk16 L114P reduces glucose- and tolbutamide-stimulated islet Ca2+ entry and augments IP3-induced islet [Ca2+]ER release.
A. and B. Representative [Ca2+]c traces in islets from male (A) and female (B) WT and Kcnk16 L114P(L/P) mice in response to 2 mM G, 10 mM G, and 20 mM G. C-F. Average normalized Ca2+ peak (C. and E.) and total AUC (D. and F.) in response to the indicated glucose concentrations in islets from male and female WT and Kcnk16 L114P(L/P) mice (N=3–4/genotype). G. Representative [Ca2+]c traces in islets from WT and Kcnk16 L114P(L/P) male mice in response to 100 μM tolbutamide followed by 30 mM KCl stimulation. H. Average AUC of normalized [Ca2+]c during 100 μM tolbutamide or 100 μM tolbutamide with 30 mM KCl stimulation (N=3 mice/genotype). I. Representative [Ca2+]c traces in response to 100 μM acetylcholine in the absence of extracellular Ca2+ in islets from male WT and Kcnk16 L114P(L/P) mice. J. Average AUC of normalized [Ca2+]c following 100 μM acetylcholine stimulated [Ca2+]ER release (N=876 cells; WT, N=513 cells; Kcnk16 L114P (L/P)). Data are presented as mean±SEM. Data were analyzed using student’s t-test.