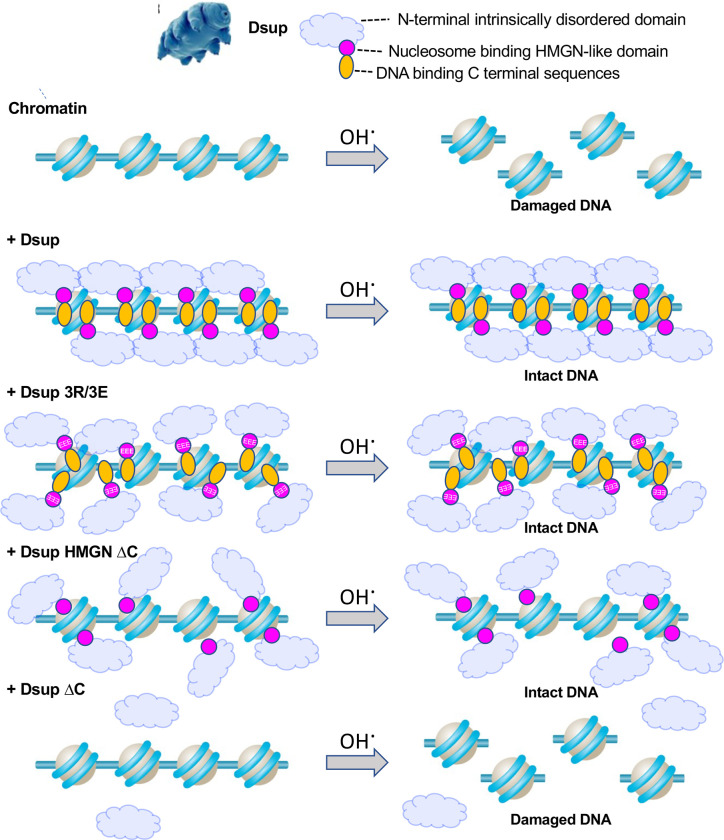
Fig. 8. Model for multivalent association of Dsup with the genome to protect from oxidative DNA damage.
Multivalent binding of Dsup to the chromatinized genome protects against oxidative DNA damage (as exogenously induced by H2O2). Dsup mutations that independently diminish interaction with the nucleosome acidic patch / histone tails (HMGN-like domain; pink), or DNA (C-terminal distal sequences; orange) have reduced chromatin interaction but are still capable of protecting the genome against H2O2-mediated DNA damage. However, loss of both interacting regions ablates the Dsup interaction with chromatin, and thus its ability to protect from oxidative DNA damage.