Figure 2. Suppressive functionality in tTex cells can act on multiple target cells and is environment-dependent.
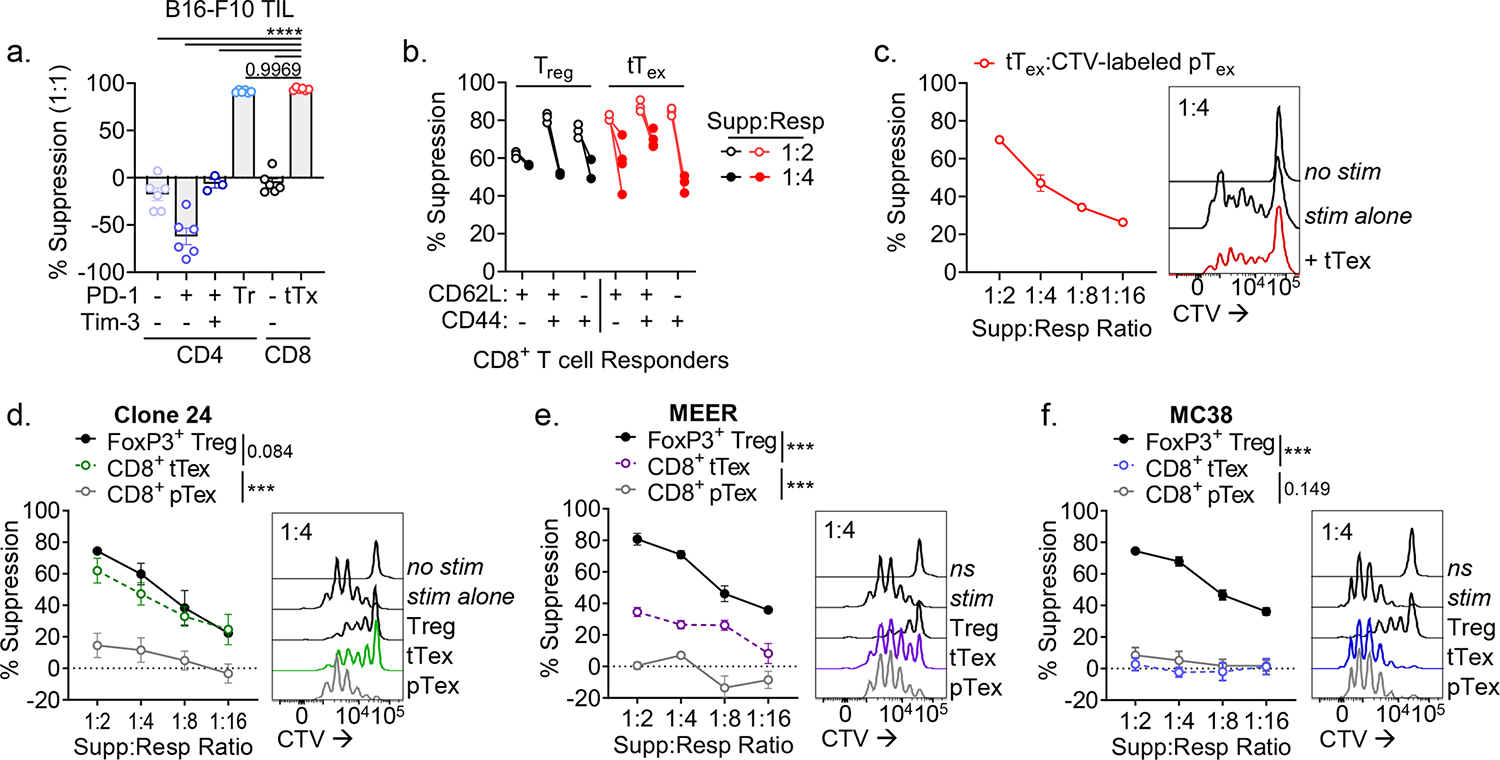
(A) CD4+ and CD8+ TIL populations from B16-F10 tumors stratified by inhibitory receptor expression and utilized as the ‘suppressor’ group in ex vivo suppression assay. (B) Suppression assay utilizing diverse responder populations from tumor draining lymph nodes and co-cultured with PD-1hiTim-3+ tTex cells or Foxp3+ Treg cells. (C) Proliferation dye labeled pTex cells co-cultured with tTex cells in repeat suppression assays. (D-F) Suppression assay with TIL from (D) Ptenf/fBRafLSL.V600ETyr2Cre.ER–derived melanoma clone, dubbed Clone 24, (E) PD-1-resistant MEER head and neck carcinoma, or (F) PD-1-sensitive MC38 adenocarcinoma. Statistics are one-way ANOVA (A) and linear regression (D-F) with *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 and ****p<0.0001.
