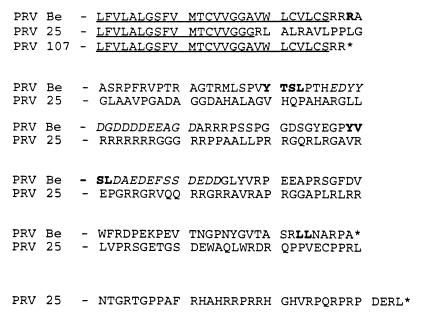
FIG. 1.
Amino acid comparison of gE proteins. The amino acid sequences of the transmembrane domains and cytoplasmic tails of gE proteins encoded by PRV Be (wild-type), PRV 25 (frameshift), and PRV 107 (Am457) are shown. The transmembrane domain of each protein is underlined. Potential internalization motifs, either tyrosine or dileucine based, are in shown in bold in the wild-type sequence. The two acidic amino acid clusters are shown in italics. An asterisk indicates a stop codon in translation of the protein. PRV 25 contains a shift in reading frame predicted to result in a truncated transmembrane domain and a novel cytoplasmic tail. PRV 107 contains an amber stop codon in place of an arginine residue just after the transmembrane domain and encodes a truncated, anchored gE protein.