Fig. 2. The UBR5 dimer structure.
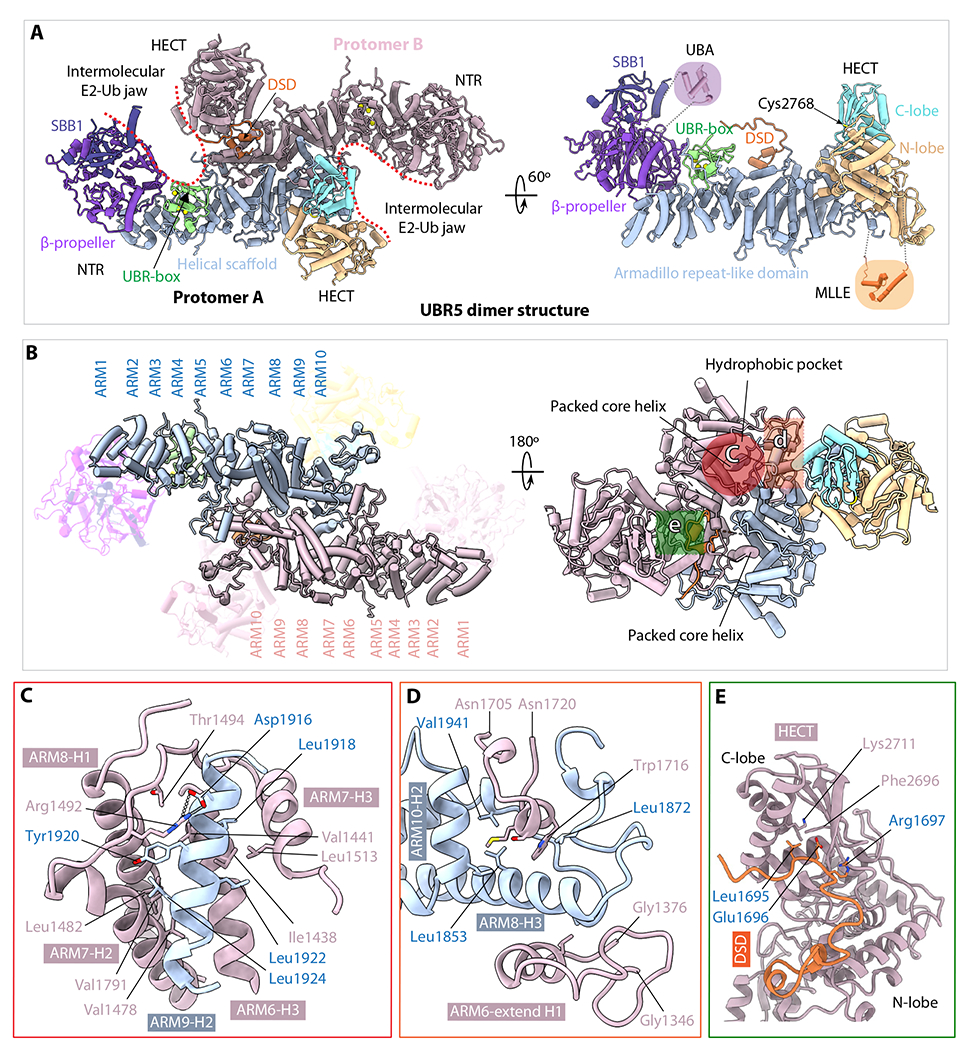
(A) The dimer structure in cartoon viewed from top along the 2-fold symmetry axis (left) and a monomer in a side view (right). Th structures are colored as in Figure 1A. The crystal structures of the UBA (PDB ID 2QHO) and MLLE (PDB ID 3NTW) are shown in shadowed cartoons for illustrative purpose only; they are invisible in the EM map. (B) Top and bottom views of the middle Armadillo-like helical scaffold that primarily mediates UBR5 dimerization. The three major interacting regions are marked by three colored shapes in the right panel. (C) Close-up view of the hydrophobic interface region marked by the red circle in (B). Residues involved in dimerization such as the salt bridge between Arg1492 and Asp1916 are shown as sticks. (D) Close-up view of the interface region marked by the orange square in (B). This region contains both hydrophobic and H-bonding interactions. (E) Close-up view of the region marked by green square in (B), which involves the domain-swapped dimerization (DSD) motif.
