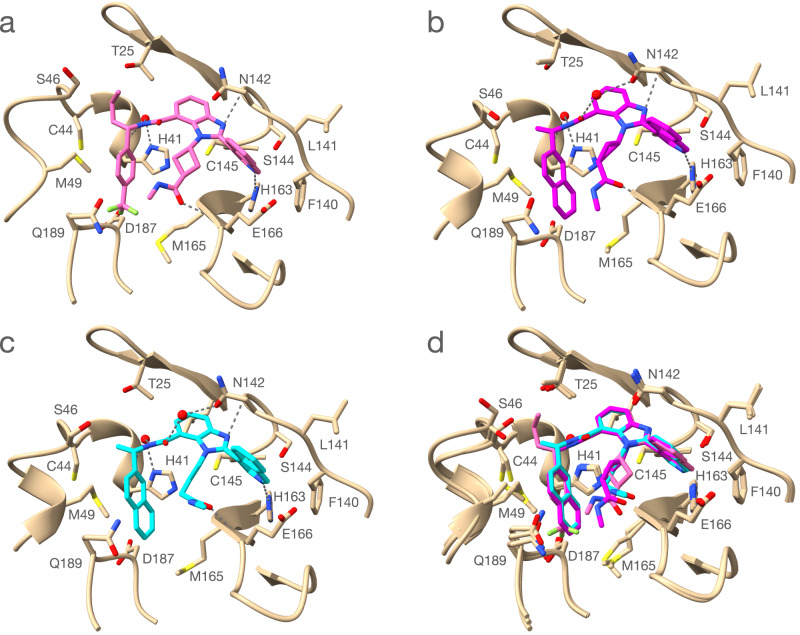
Fig. 3. Crystal structure of Mpro in complex with CDD-1733 (PDB: 7URB), CDD-1819 (PDB: 7US4) and CDD-1845 (PDB: 7UR9).
a Structure of Mpro (Tan) with CDD-1733 (pink). Carbon atoms of the inhibitor are pink, nitrogen atoms are blue and oxygen atoms are red. The Mpro amino acid residues involved in CDD-1733 binding are shown as stick models and labeled. Hydrogen bonds are indicated with dashed gray lines. A water molecule (red sphere) involved in a hydrogen bond from CDD-1733 bridging to the carbonyl oxygen of His41 is shown. b Structure of Mpro (Tan) with CDD-1819 (magenta). Carbon atoms of the inhibitor are magenta, nitrogen atoms are blue and oxygen atoms are red. The Mpro amino acid residues involved in CDD-1819 binding are shown as stick models and labeled. Two water molecules involved in hydrogen bond (colored red) from bridging hydrogen bonds to His41 O and the side chain O of Asn142. c Structure of Mpro (Tan) with CDD-1845 (light blue). Carbon atoms of the inhibitor are light blue, nitrogen atoms are blue and oxygen atoms are red. The Mpro amino acid residues involved in CDD-1845 binding are shown as stick models and labeled. Two water molecules involved in hydrogen bond (colored red) from bridging hydrogen bonds to His41 O and the side chain O of Asn142. d Alignment of Mpro structures with bound CDD-1733, CDD-1819, and CDD-1845. Hydrogen bonds are omitted for clarity.