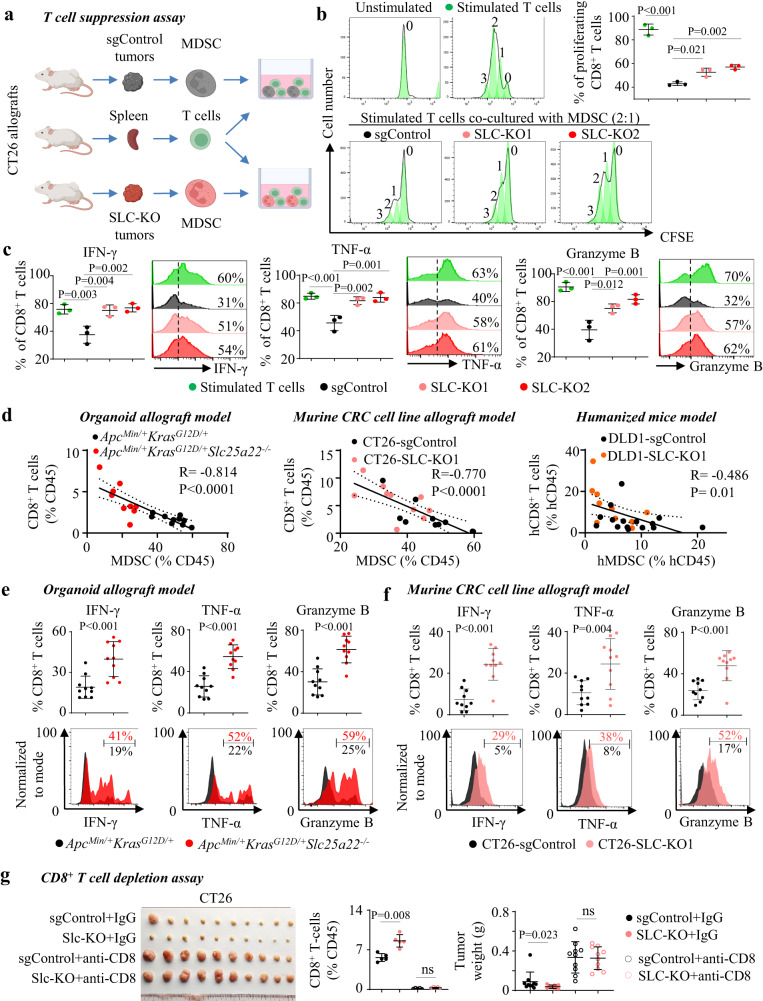
Fig. 5. SLC25A22-mediated MDSC recruitment represses T-cell proliferation and activation.
a Workflow of T-cell suppression assay. b T-cell suppression assay showed that MDSC isolated from CT26-Slc-KO allografts have attenuated ability to suppress T-cell proliferation (n = 3) and c expression of cytotoxic markers IFN-γ, TNF-α, and Granzyme B (n = 3). Each dot represents an independent sample. d Tumoral MDSC negatively correlated with CD8+ T cells in ApcMin/+KrasG12D/+ allografts (n = 10), CT26 allografts (n = 10), and DLD1 xenografts (sgControl, n = 15; SLC-KO, n = 10). Each dot represents an independent tumor. e In ApcMin/+KrasG12D/+ organoid allografts (n = 10) and f CT26 allografts (n = 10), SLC25A22 knockout increased the tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells expressing activation marker (IFN-γ, TNF-α, and Granzyme B). Each dot represents an independent tumor. g CD8+ T cells depletion with anti-CD8 antibody abrogated growth inhibition by SLC25A22 knockout in CT26 allograft (n = 10). Each dot represents an independent mouse (left) or tumor (right). Data are shown as mean ± SD (b, c, e–g). Two-tailed one-way ANOVA (b, c). Two-tailed Student’s t test for two-group comparison (e, f). Two-tailed Mann–Whitney U test g. Two-tailed Pearson correlation test d. ns, no significance. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.