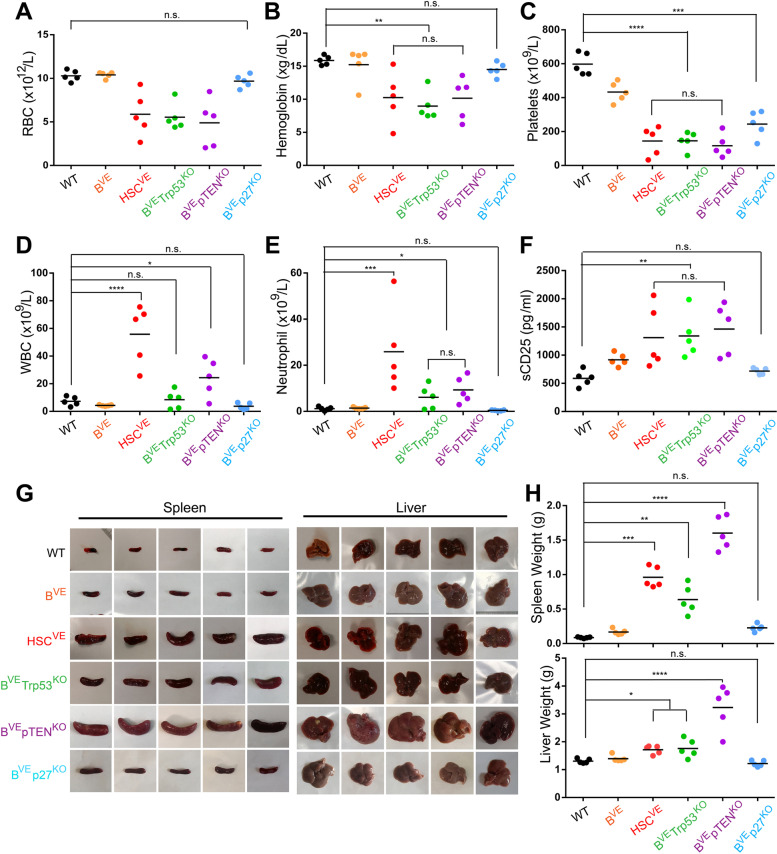
Fig. 2.
BVETrp53KO or BVEpTENKO but not BVEP27KOmice develop hematopoietic disorders with splenomegaly and hepatomegaly like HSCVE mice. A-E Blood parameters were altered in HSCVE, BVEP53−/−, and BVEPTEN−/− mice but not BVEP27−/− mice. Blood was collected from the tail veins of mice with terminal disease (HSCVE, 8 ~ 12 weeks; BVEP53−/−, 25 ~ 30 weeks; and BVEPTEN−/−, 16 ~ 20 weeks) and blood parameters were measured with a hematology analyzer. A, Red blood cell counts; B, hemoglobin counts; C, platelet counts; D, white blood cell counts; and E, neutrophil counts of mice at the late stage of disease (n = 5, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001; n.s., not significant). F High level of sCD25 was indicated in HSCVE, BVEP53−/−, and BVEPTEN−/− mice but not in BVEP27−/− mice. The serum concentration of sCD25 in mice with late disease stage was measured by ELISA (n = 5, **p < 0.01; n.s., not significant). G-H HSCVE, BVEP53−/−, and BVEPTEN−/− mice developed splenomegaly and hepatomegaly. The spleens and livers of mice with terminal stage disease were harvested (G) and weighed (H) at the experimental end point. In all experiments, 28-week-old wild type or BVE or BVEP27−/− mice served as controls (n = 5, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001; n.s., not significant)