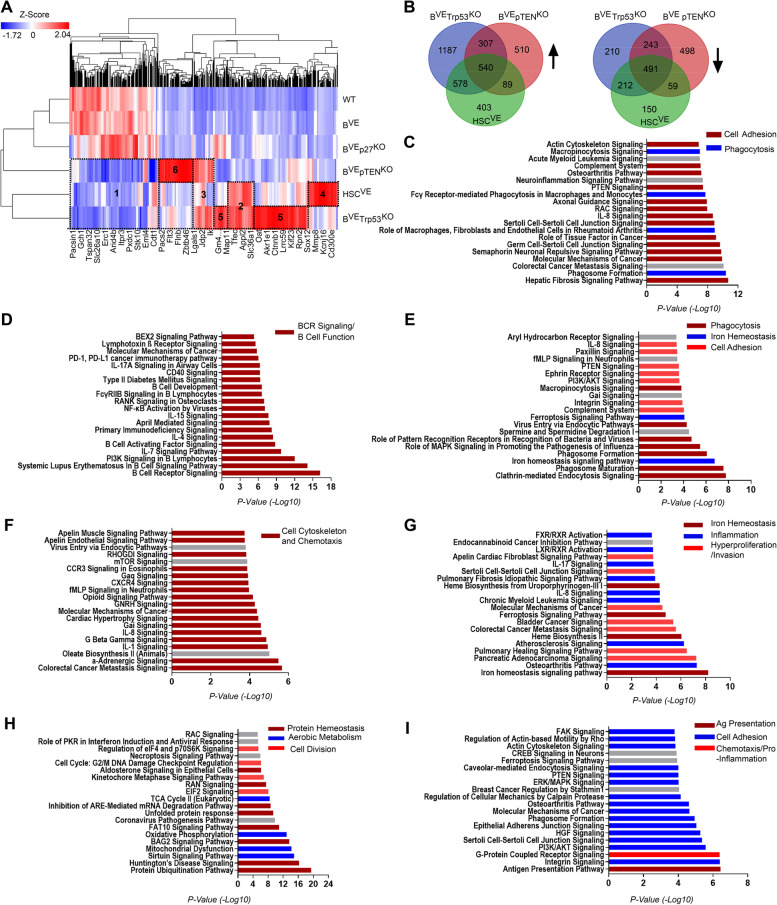
Fig. 5.
Splenic BVETrp53KO or BVEpTENKO leukemic cells have unique gene expression signatures. A The lineage-specific gene expression signatures in HSCVE, BVEP53−/− or BVEPTEN−/− leukemic cells were explored by RNA-seq analysis. RNA samples (three samples per group) were extracted from purified splenic B cells and were analyzed by next-generation sequencing. The hierarchical clustering heatmap was generated as described in Materials and Methods. Signature #1, gene clusters down-regulated in all three leukemic cells; Signature #2, gene clusters up-regulated in HSCVE and BVEP53−/− leukemic cells; Signature #3 gene clusters up-regulated in BVEP53−/− and BVEPTEN−/− leukemic cells; Signature #4, #5, and #6, lineage-specific gene clusters up-regulated in HSCVE, BVEP53−/− or BVEPTEN−/− leukemic cells. B A Venn diagram of genes that were up-regulated (upper panel) or down-regulated (lower panel) in HSCVE, BVEP53−/− and BVEPTEN−/− leukemic cells. C-I Differential cellular programs were turned on in HSCVE, BVEP53−/− and BVEPTEN−/− leukemic cells. Ingenuity pathway analyses (IPA) of prominent gene signatures of HSCVE, BVEP53−/− or BVEPTEN−/− leukemic cells shown in the hierarchical heatmap (A) or the Venn diagrams (B) was calculated as described in the Materials and Methods, and then the pathways that regulate approximate cellular function were categorized accordingly. C-D, Cellular activities were enhanced (C) or dampened (D) in all three leukemic cells. E-F, Cellular activities were up-regulated in HSCVE and BVEP53−/− leukemic cells (E) or BVEP53−/− and BVEPTEN−/− leukemic cells (F). G-I, Cellular activities were elevated in HSCVE leukemic cells (G), or BVEP53−/− leukemic cells (H), or BVEPTEN−/− leukemic cells (I). In all experiments, splenic B cells were isolated from mice with terminal stage disease or mice without disease at 28 weeks. All data are representative of three mice per group