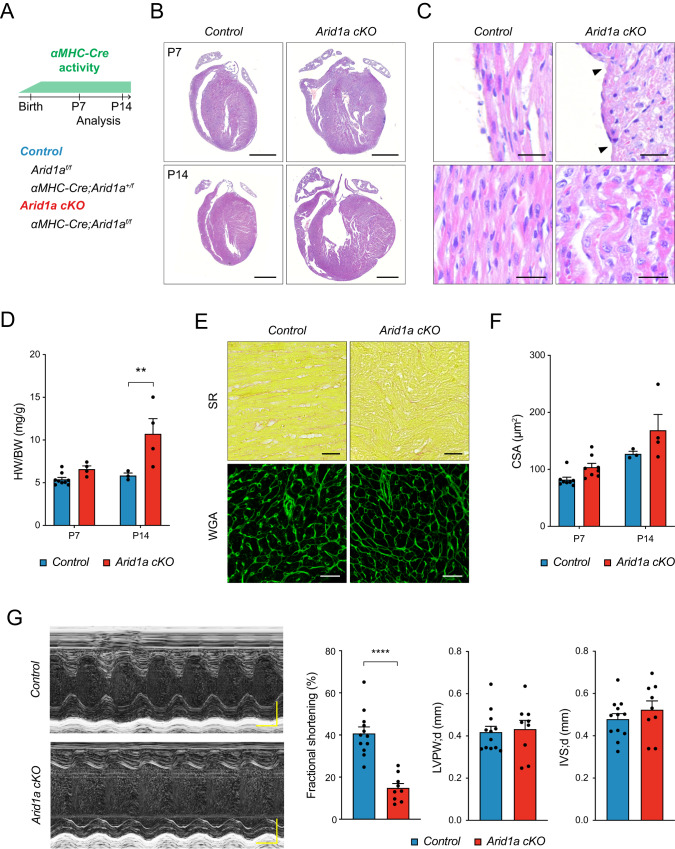
Fig. 2. Arid1a is required in neonatal cardiomyocytes for heart maturation.
A Schematic showing analysis timeline for cardiomyocyte specific Arid1a mutants (Arid1a cKO). B Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of P7 and P14 control and Arid1a cKO hearts. C Uneven surface (arrowheads) and signs of myocardial disarray (bottom) in Arid1a cKO hearts (n = 4) compared to controls (n = 5) at P14. D Heart weight to body weight ratio (HW/BW) at P7 (Control, n = 9; Arid1a cKO, n = 4) and P14 (Control, n = 3; Arid1a cKO, n = 4; P = 0.0029; **P < 0.01, two-way ANOVA with Šídák’s multiple comparisons test). E Sirius red (SR) staining for fibrosis and wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) staining for extracellular matrix. F Quantification of cardiomyocyte cross-sectional area (CSA) as measured from WGA-stained hearts at P7 (n = 8) and P14 (Control, n = 3; Arid1a cKO, n = 4) revealed no significant difference between Arid1a cKO and control at P7 (P = 0.2049) or P14 (P = 0.1021; two-way ANOVA with Šídák’s multiple comparisons test). G Representative example of echocardiography analysis of cardiac function in P7 hearts, with quantification of fractional shortening (P < 0.0001), interventricular septum thickness (IVS; P = 0.7787) and left ventricular peripheral wall thickness (LVPW; P = 0.3624) during diastole (d) (Control, n = 12; Arid1a cKO, n = 9; ****P < 0.0001, two-tailed Student’s t-test). Scale bars 1 mm (B), 25 µm (C), 50 µm (E), 0,1 s (G, horizontal), 0,1 mm (G, vertical). All bar graphs show mean with standard error of the mean. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.