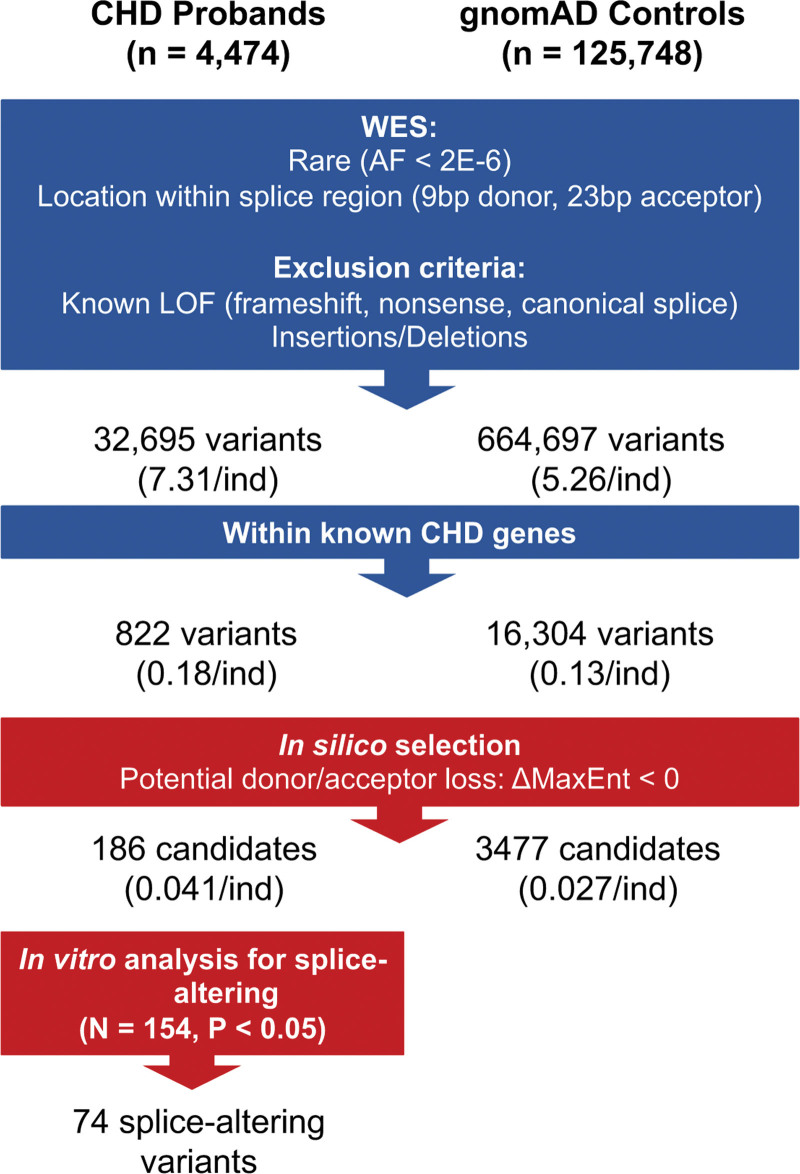
Figure 2.
Schematic of the analyses of putative rare RNA splice-altering variant candidates in congenital heart disease (CHD) probands and gnomAD controls. We restricted functional analyses to rare (allele frequency [AF], <2×10−6 in gnomAD) single-nucleotide variants residing within 9 bp of donor and 23 bp acceptor regions of CHD genes in 4474 CHD and 125 748 gnomAD controls. Based on computational prioritization of variants likely to cause the loss of donor or acceptor splice (calculated ΔMaxEnt score, <0), we studied 186 (22.6%) using an in vitro splicing assay and identified 74 as splice altering. Parallel processing of variants in gnomAD controls identified 664 697 variants within splice sequences, of which 16 304 were encoded in CHD genes. Computational prioritization using MaxENT scores identified 3477 candidate variants (2301 within 9 bp of 5′ donor splice sequences and 1176 within the 23 bp of 3′ acceptor sequences). gnomAD candidate variants were not assessed in the minigene assay.