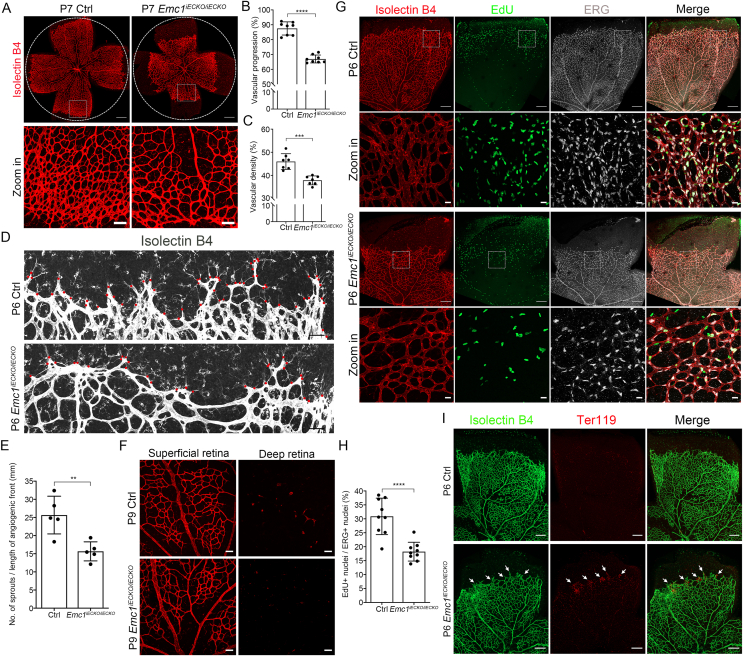
Figure 1.
Loss of Emc1 in mouse endothelial cells results in retinal vascular defects. (A) Representative overview (top panels) and high-magnification images (bottom panels) of P7 control (Ctrl) and Emc1iECKO/iECKO mouse retinae stained with Isolectin B4 (IB4). The circles indicate vessel outgrowth of Ctrl retinae. Scale bars, 500 μm and 100 μm. (B, C) Quantification of vascular progression (B) and vascular density (C) of P7 control (Ctrl) and Emc1iECKO/iECKO mouse retinae. Error bars, standard deviations (SDs). Student's t-test (n ≥ 7), ∗∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001. (D) Representative immunofluorescence images of P6 Ctrl and Emc1iECKO/iECKO mouse retinae stained with IB4. Red dots indicate sprouts at the angiogenic front. Scale bars, 50 μm. (E) Quantification of the numbers of sprouts per unit of front length (mm). Error bars, SDs. Student's t-test (n = 5), ∗∗P < 0.01. (F) Representative immunofluorescence image of superficial and deep IB4-staining retinae of P9 Ctrl and Emc1iECKO/iECKO mice. Scale bars, 50 μm. (G) Representative overview and high-magnification images of P6 Ctrl and Emc1iECKO/iECKO mouse retinae co-stained with IB4, EdU, and ERG. Dotted boxes indicate magnified areas. Scale bars, 20 μm and 200 μm. (H) Quantification of the percentage of EdU+/ERG + cells to total ERG + cells per field. Error bars, SDs. Student's t-test (n = 9), ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001. (I) Representative immunofluorescence images of P6 Ctrl and Emc1iECKO/iECKO mouse retinae co-stained with IB4 and Ter119. White arrows indicate leakage of erythrocytes. Scale bars, 200 μm.