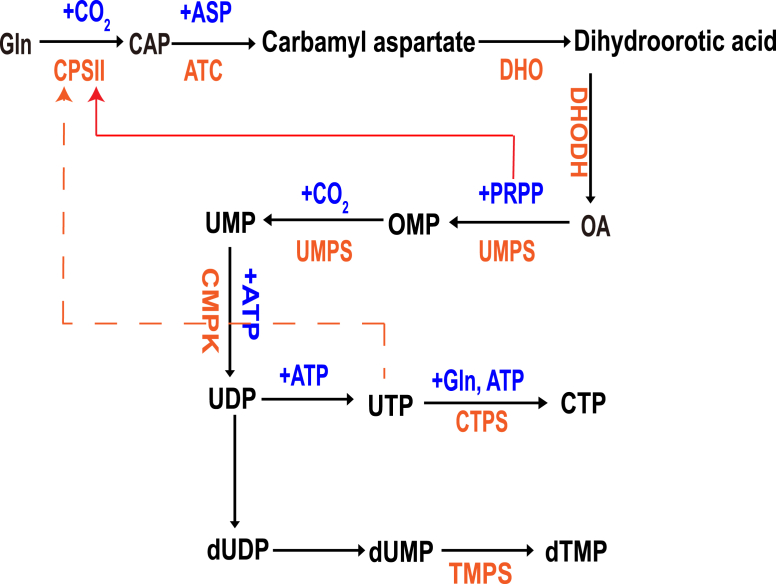
Figure 2.
De novo pyrimidine biosynthetic pathway. The first step of pyrimidine synthesis is to produce carbamoyl phosphate. Carbamoyl phosphate synthase Ⅱ (CPS Ⅱ) catalyzes the condensation of CO2 and glutamine. Aspartate carbamoylase (ATCase) catalyzes the condensation of aspartic acid and carbamoyl phosphate to produce carbamoyl aspartate. This reaction is the rate limiting step of pyrimidine synthesis. ATCase is a rate limiting enzyme, which is inhibited by the feedback of the product. It does not consume ATP and is powered by carbamoyl phosphate hydrolysis. Dihydro whey acid with pyrimidine ring was formed by dehydration and intramolecular rearrangement of carbamoyl aspartic acid catalyzed by dihydro whey enzyme. Catalyzed by dihydroorotate reductase, dihydroorotate is oxidized to orotate. This enzyme requires FMN and non heme Fe2+, which is located on the outer side of the mitochondrial inner membrane. Quinones provide oxidation ability. The other five enzymes in pyrimidine synthesis exist in the cytosol. The reaction of whey acid with PRPP was catalyzed by whey acid phosphoribosyltransferase to produce orotidine-5 ′- monophosphate (OMP). It is powered by PRPP hydrolysis. OMP decarboxylase catalyzes OMP decarboxylation to produce UMP. The synthesis of uridine triphosphate (UTP) is similar to that of purine nucleoside triphosphate. Cytidine triphosphate (CTP) is produced by ammonia addition of UTP catalyzed by CTP synthase. In animals, the amino group is provided by glutamine, while in bacteria, it is directly provided by NH3. This reaction consumes 1 ATP.