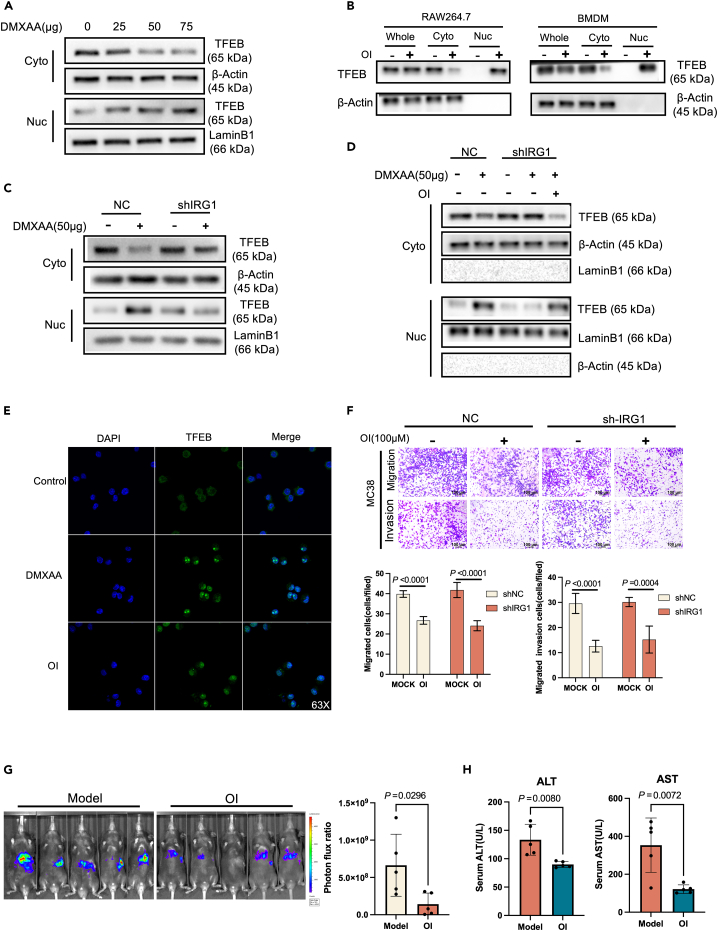
Figure 9.
STING induces TFEB into the nucleus after activating IRG1
(A) Western Blot analysis of BMDM treated with different concentrations of DMXAA (0 μg,25 μg,50 μg,75 μg), the expression difference of TFEB in the cytoplasm and nucleus (β-Actin is a cytoplasmic internal reference protein, LaminB1 is a nuclear internal reference protein).
(B) Western Blot analysis of TFEB expression differences in cytoplasm and nucleus after RAW264.7 and BMDM cells were treated with 150 μM OI (4-Octyl Itaconate) for 4 h (β-Actin is a cytoplasmic internal reference protein, LaminB1 is a nuclear internal reference protein), Whole: total cell protein, Cyto: cytoplasmic protein, Nuc: nuclear protein.
(C) Western Blot analysis of TFEB protein expression difference in cytoplasm and nucleus after knockdown of IRG1 in RAW264.7 cells after 50 μg DMXAA treatment.
(D) Western Blot detection of TFEB protein expression in RAW264.7 cells after IRG1 knockdown.
(E) Immunofluorescence detection of nuclear translocation of TFEB protein after RAW264 cells were treated with 50 μg/mL DMXAA or RAW264.7 cells were treated with 150 μM OI (4-Octyl Itaconate).
(F) After RAW264.7 knocked down IRG1, polarization was induced by IL4, and the migration and invasion of MC38 cells were detected after being treated with OI for 4 h and co-cultured with MC38 for 48 h in a transwell chamber.
(G) After spleen injection of MC38-Luc cells to construct a colorectal cancer liver metastasis model, the liver metastasis model mice were treated with OI (i.p.) (50 mg/kg/2 day) or PBS for 3 weeks. Bioluminescence signal imaging (left) and quantitative analysis of bioluminescence (right) in representative mice, n ≥ 5.
(H) ALT and AST levels in peripheral blood of mice with colorectal cancer liver metastases after 3 weeks of OI or PBS treatment.