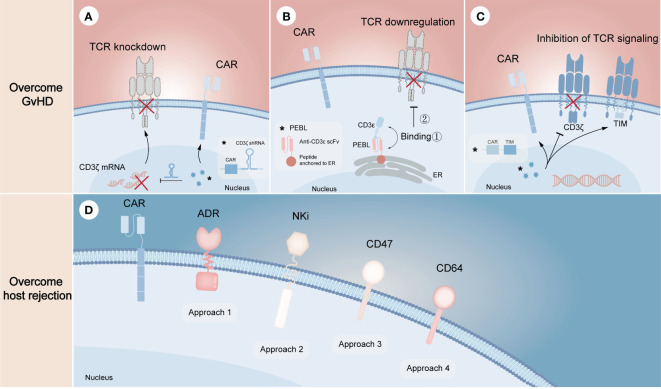
Figure 3.
Non-gene editing technologies for overcoming GvHD and host-mediated allorejection. The above (A–C) represents the strategies to overcome GvHD, illustrating the knockdown of TCR complex through CD3ζ mRNA silencing (A), the downregulation of TCR complex through expressing a CD3ϵ-specific PEBL that retaining the complex in cytoplasm (B), and the inhibition of TCR signaling by expressing TIM molecules that can competitively replace CD3ζ when binding αβ TCR (C). The below (D) represents the strategies to overcome host rejection, in which approach 1-4 show the expression of ADR for evading the killing of host T and NK cells, the expression of NKi to inhibit the activation of host NK cells and thus to reduce NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity, the overexpression of CD47 to escape host NK cell-mediated rejection, the overexpression of CD64 to escape antibody-mediated rejection, respectively. The symbol “*” represents the general schematic of a molecule (e.g., labeled virus particles (blue) in A) and its specific structure or composition (e.g., labeled white box in A).