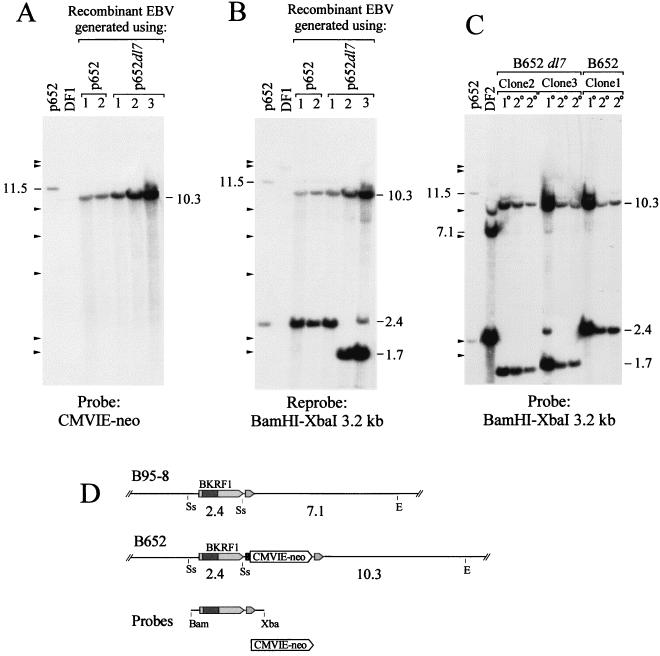
FIG. 2.
Southern analysis of EBV genomes carrying the inserted CMVIE-neo gene and a deletion of IR3 in immortalized B-cell clones. (A) B cells were immortalized with recombinant EBV that was generated by using each indicated plasmid. Five micrograms of total cellular DNA was digested with EcoRV plus SstII. The blot was probed with the CMVIE-neo gene. To the left, 294 pg of digested p652 DNA was used, corresponding to 9 DNA molecules per cell. For p652, the CMVIE-neo gene is on an 11.5-kb SstII-EcoRV fragment; its position is indicated. (B) The blot was stripped and reprobed with a BamHI-XbaI fragment spanning the EBNA-1 gene. DF1 is an EBV-immortalized B-cell line that carries between 5 and 10 EBV genomes per cell. Cytosine methylation at several SstII sites can account for the large size of the major band and for the partial digestion seen with DF1. (C) Southern analysis of two secondary B-cell clones (2°) that were obtained by using virus released from each of the primary isolates (1°), clones 1, 2, and 3, that were analyzed for panels A and B. DNA was digested with EcoRV plus SstII as for panels A and B and probed with the BamHI-XbaI 3.2-kb fragment. DF2 is an EBV-immortalized B-cell line that contains approximately 100 EBV genomes per cell. Marks to the left of A, B, and C indicate size markers (bacteriophage lambda DNA cut with HindIII). (D) Restriction maps of the relevant portion of the EBV genome for strain B95-8 and for B652. Cleavage sites for SstII (Ss) and EcoRV (E) and the sizes of fragments from the double digest, in kilobase pairs, are indicated; see the legend to Fig. 1 for details. DNAs used to make hybridization probes are shown below.