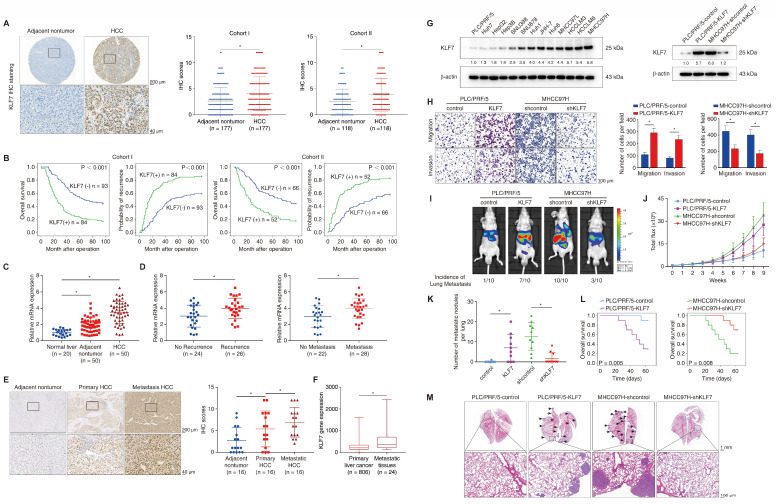
Figure 1.
KLF7 overexpression indicates poor prognosis in HCC patients and promotes HCC metastasis. (A) Representative IHC images and IHC scores of KLF7 staining in para-cancerous nontumor specimens and HCC specimens in two independent microarrays. (B) Kaplan-Meier analysis of the correlation of KLF7 expression with overall survival and recurrence in two independent HCC cohorts. (C) Relative KLF7 mRNA expression in 20 normal liver samples and 50 pairs of para-cancer nontumor and HCC tissues. (D) The mRNA expression of KLF7 in primary HCC samples from patients without or with recurrence (left) and metastasis (right). (E) Representative IHC pictures and IHC scores of KLF7 staining in adjacent nontumorous samples, HCC samples, and matched metastatic HCC samples. (F) The gene expression of KLF7 in primary live tumors (n = 806) and liver cancer metastatic tissues (n = 24) was analyzed. Data from the TNMplot database (https://tnmplot.com/analysis/). (G) The protein levels of KLF7 in human HCC cell lines (left). KLF7 upregulation and knockdown in indicated HCC cells after lentiviral transfection were confirmed by immunoblotting (right). (H) The motility of indicated HCC cell lines with KLF7 expression changes were detected by transwell assays. (I-M) Effect of KLF7 overexpression on HCC metastasis were evaluated by orthotopic HCC models. (I) Representative bioluminescent images of hepatic tumors and incidence of pulmonary metastases. (J) Dynamic intensity of bioluminescent signals of liver tumors. (K) Number of lung metastatic nodules. (L) Overall survival time of nude mice. (M) Representative H&E staining of lung tissues. *P < 0.05. Abbreviations: IHC, Immunohistochemical; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin.