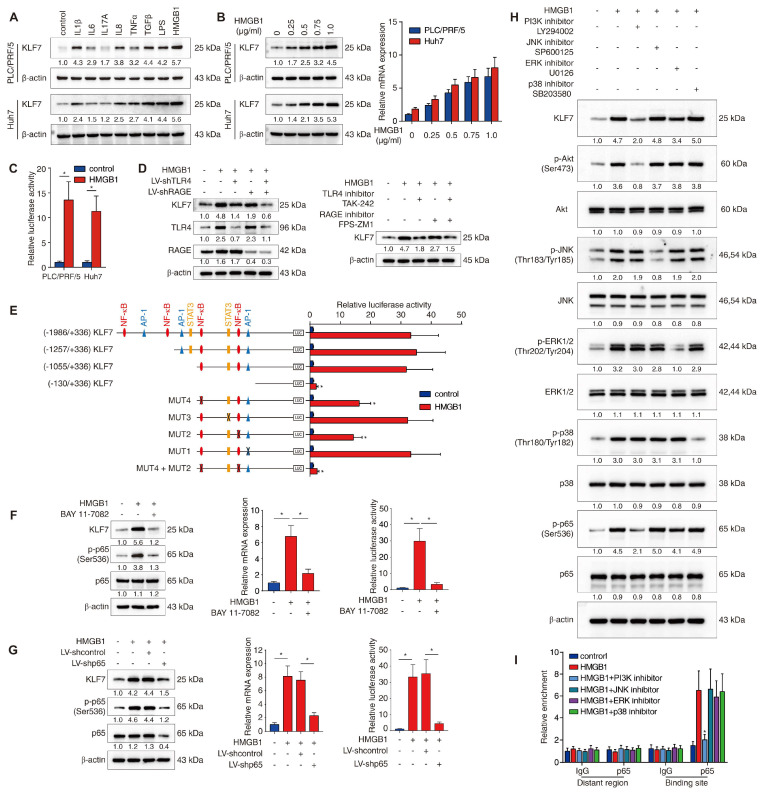
Figure 4.
HMGB1 induces KLF7 expression through the TLR4/RAGE-PI3K-AKT-NF-κB signaling pathway. (A) PLC/PRF/5 and Huh7 cells were incubated with a panel of inflammatory factors for 24 hours, and KLF7 expression was then examined. (B) Western blotting and real-time PCR analysis of KLF7 expression in PLC/PRF/5 and Huh7 cells after HMGB1 treatment at a series of gradient doses for 24 hours. (C) The luciferase reporter activity of the KLF7 promoter was measured in PLC/PRF/5 and Huh7 cells treated with HMGB1. (D) PLC/PRF/5 cells were transfected with LV-shTLR4, LV-shRAGE or a combination before HMGB1 treatment, KLF7, TLR4 and RAGE expression were then detected (left). TLR4 and RAGE inhibitors were applied in PLC/PRF/5 cells under HMGB1 treatment, and KLF7 expression was then examined (right). (E) PLC/PRF/5 cells were transfected with serially truncated or mutated KLF7 promoter constructs and treated with or without HMGB1. Luciferase reporter activities were then detected. (F-G) PLC/PRF/5 cells were treated with NF-κB inhibitor BAY 11-7082 (F) or transfected with LV-shp65 (G) before HMGB1 stimulation. KLF7 expression and KLF7 promoter activity were measured by western blotting, real-time PCR and luciferase reporter assays. (H) PLC/PRF/5 cells were precultured with inhibitors specific to PI3K, JNK, ERK and p38 before HMGB1 treatment. KLF7 expression as well as the levels of phosphorylated and total AKT, JNK, ERK, p38 and p65 were then detected. (I) A ChIP assay was conducted to examine the relative enrichment of p65 on the KLF7 promoter when PLC/PRF/5 cells were treated with HMGB1 and inhibitors of PI3K, JNK, ERK and p38.