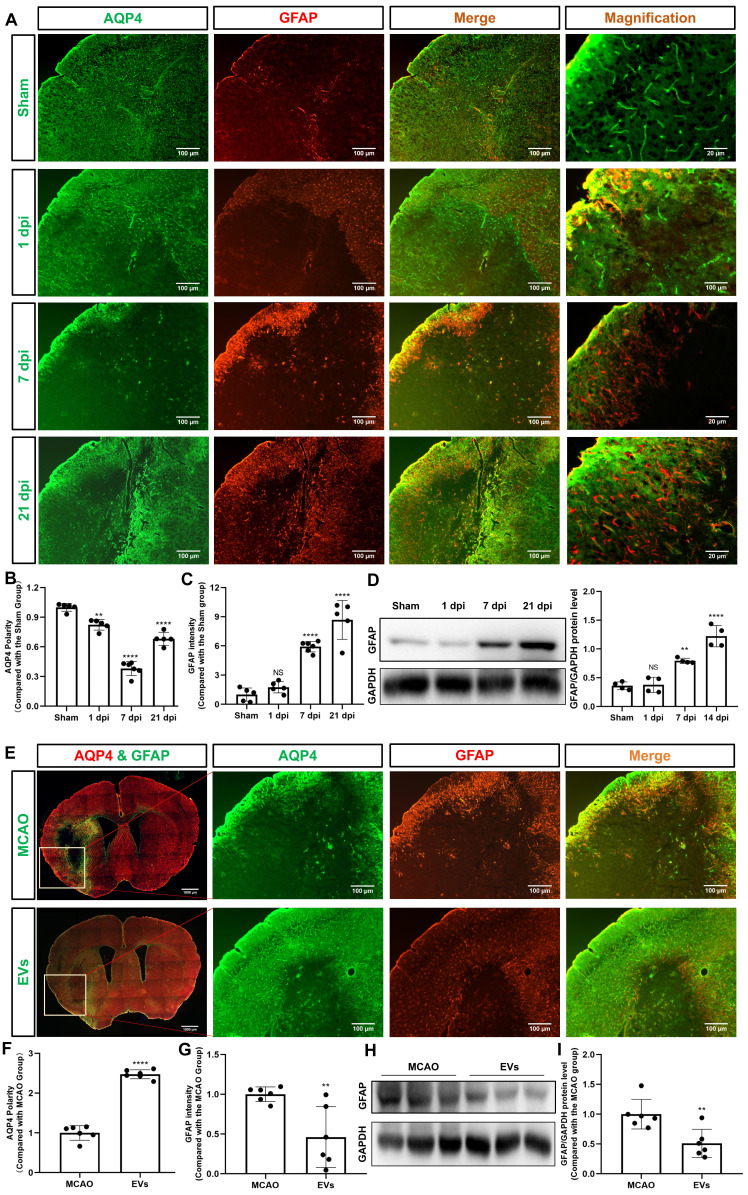
Figure 3.
EVs from hypoxic microglia abrogate AQP4 depolarization and reactive astrogliosis in the periinfarct cortex. (A) Dynamic evolution of AQP4 polarity and GFAP fluorescence in the periinfarct cortex. (B-C) Statistical plots of AQP4 polarity and GFAP mean fluorescence intensity in the periinfarct cortex of different groups of mice (n = 5-6). The polarity of AQP4 decreased significantly at all time points compared with the sham group. The GFAP intensity was boosted on dpi7 and dpi21. (D) The dynamic GFAP protein expression in the ischemic cortex on dpi1, 7, and 21 was measured by western blot. Compared with the sham group, the protein expression of GFAP on dpi1 was not significantly increased, whereas the protein expression of GFAP on dpi7 and dpi21 were significantly increased (n = 4). (E) Schematic diagram of the cortex of interest along with representative immunofluorescence maps among the MCAO+PBS and EV treatment groups. The white boxes represent the region of interest. (F-G) Statistical analysis of the polarity of AQP4 and GFAP intensity. The EV treatment group was associated with a higher AQP4 polarity and a lower GFAP intensity in the ischemic cortex on dpi7 (n = 6). (H-I) The impact of EV treatment on GFAP protein level in the ischemic cortex on dpi7 was measured by western blot (n = 6). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001; NS, not statistically significant; MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion; EVs, extracellular vesicles; AQP4, aquaporin 4; dpi, day post-ischemia; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein.