Fig. 1.
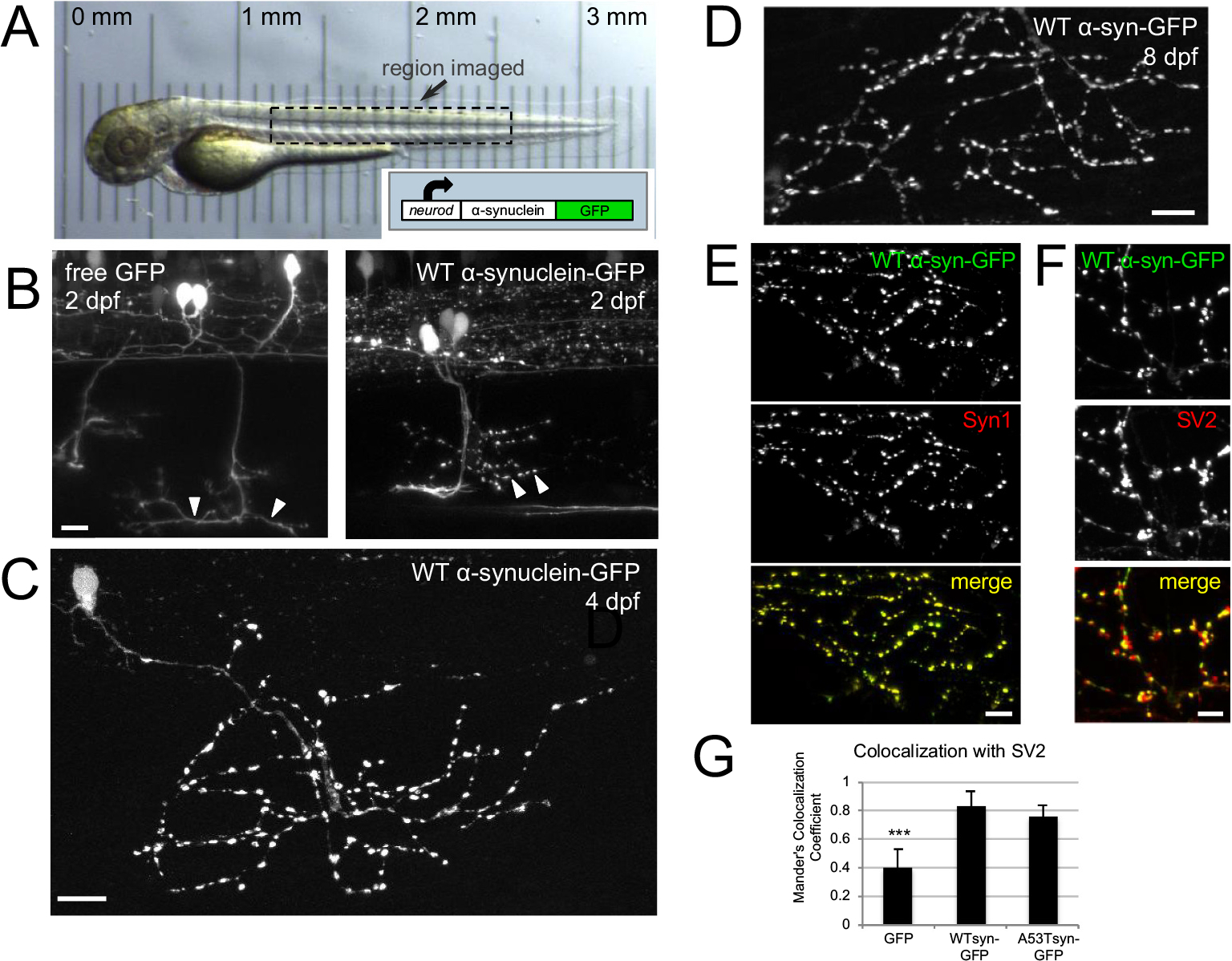
Human α-synuclein-GFP expresses in zebrafish neurons and localizes to presynaptic terminals.
A) In vivo transmitted light image of zebrafish at 2 dpf; box indicates general region targeted for imaging. Translucency of larva is demonstrated by micrometer placed below; reprinted from Brockway et al., 2019. Inset shows schematic of neurod:α-synuclein-GFP DNA. B) In vivo imaging at 2 dpf shows that free GFP fills axons smoothly, while α-synuclein-GFP labeling appears more punctate at presumptive synaptic terminals. Arrowheads indicate regions of axons containing synaptic terminals at 2 dpf, which become more mature by 4 dpf (C). C) WT α-synuclein-GFP expression shown at 4 dpf in fixed larvae. D) α-synuclein-GFP expression persists until at least 8 dpf (image from fixed fish). E) Expression of α-synuclein-GFP colocalizes with synuclein protein. Ventrally projecting axons of motor neuron expressing wild-type α-synuclein-GFP (top), anti-Syn1 staining (middle), and merge (bottom). Scale bars 10 μm in B-E. F-G) α-synuclein-GFP expression in motor axons correlates more strongly with presynaptic terminal marker SV2 than does free GFP. F) High magnification view of motor axons expressing wild-type α-synuclein-GFP (top), SV2 antibody staining (middle), and two-channel merge (bottom). Scale bar 5 μm. G) Average Mander’s colocalization coefficient calculated on confocal stacks shows that WT α-synuclein-GFP and A53T α-synuclein-GFP colocalize significantly more strongly with SV2 (0.83 ± 0.11, n = 4 regions from 3 larvae; and 0.77 ± 0.07, n = 5 regions from 4 larvae, respectively) than does free GFP (0.41 ± 0.12, n = 9 regions from 4 larvae; one-way ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey tests p < 0.002 and p < 0.004). In all panels, caudal is right and dorsal is up. Panels B–F are maximum intensity projections of stacks with the following depths: B) left 45 μm; B) right 36 μm; C) 56.9 μm; D) 24 μm; E) 80 μm; F) 80 μm.
