Figure 3.
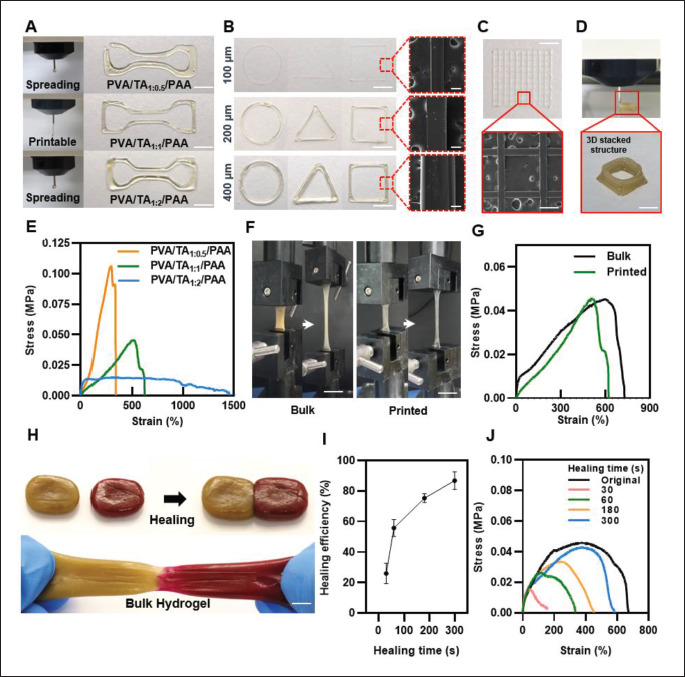
Printability and mechanical properties of hydrogel inks. (A) Photographic images of printing filament and printed structure with different mass ratios of PVA and TA. (B) 2D-printing performance of various shapes with PVA/TA1:1/PAA hydrogel inks through 400-, 200-, and 100-μm diameter nozzles, and SEM images. (C) Printed meshes structures of 2D printing and SEM image. (D) 3D-printed hydrogel by stacked structure. (E) Stress–strain curves of each ratio of printed hydrogel inks. (F) Optical image of the bulk and printed PVA/TA1:1/PAA hydrogel mechanical properties. (G) Stress–strain curves of the bulk and printed PVA/TA1:1/PAA hydrogel ink. (H) Photographs of the self-healing hydrogel. (I) Self-healing efficiency of the hydrogel as a function of healing time (n = 3: n is the sample size). (J) Stress–strain curves of self-healed hydrogel for each time point. (Scale bar: 5 mm for (B), 100 μm for SEM image of (B), 500 μm for (C), 5 mm for (D), 10 mm for (F), and 7 mm for (H)).
