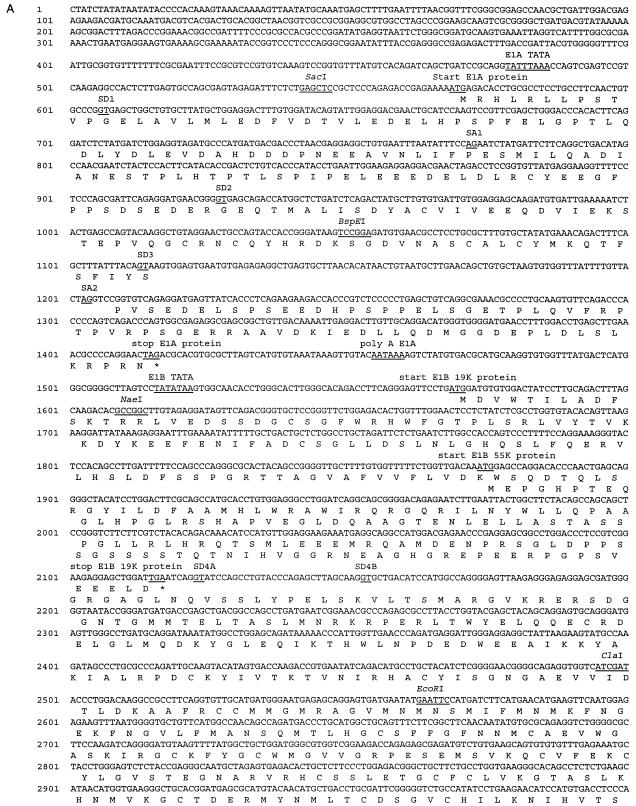
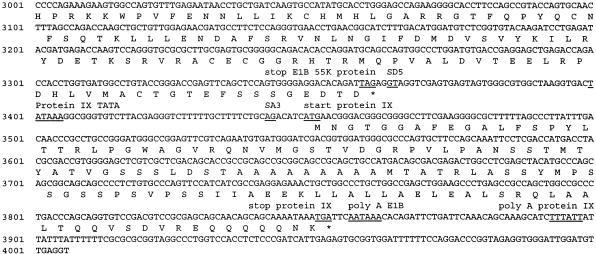
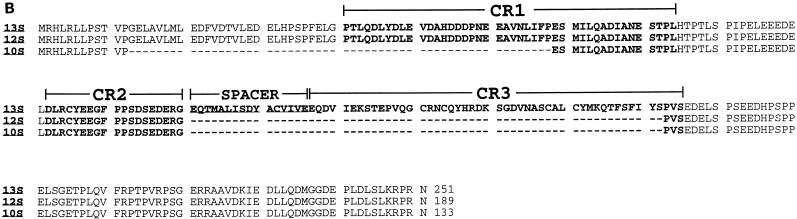
FIG. 1.
(A) Nucleotide sequence of the Ad9 E1 region. The locations of E1A, E1B, and IX gene promoter TATA boxes, known and putative splice donor (SD) and splice acceptor (SA) sites, and poly(A) signal sequences are shown. Relevant restriction enzyme sites are indicated (underlined) on the nucleotide sequence. E1A and E1B mRNA splice variants result from the use of the following SD and SA sites: 10S E1A, SD1 and SA1 plus SD2 and SA2; 12S E1A, SD2 and SA2; 13S E1A, SD3 and SA2; 13S E1B, SD4A or SD4B and SA3; and 22S E1B, SD5 and SA3. The predicted amino acid sequences of the 13S E1A, 19K and 55K E1B, and pIX polypeptides are shown beneath their coding sequences. (B) Comparison of the Ad9 13S, 12S, and 10S E1A polypeptide sequences. CR1, CR2, spacer region, and CR3 are indicated (22, 33, 48, 53).