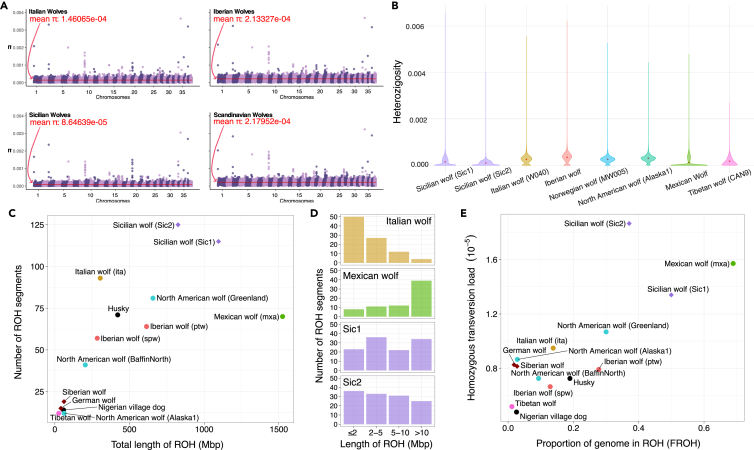
Figure 3.
Island isolation impact on the Sicilian wolf genomes
(A) Population level nucleotide diversity of Sicilian, Italian, Iberian, and Scandinavian wolves. The chromosomes and the nucleotide diversity values are shown on the x and y axis respectively. The red line represents the mean diversity value.
(B) Heterozygosity in sliding windows (excluding repetitive regions) for different wolf samples show reduced levels of heterozygosity in the Sicilian wolves Sic1 and Sic2.
(C) Individual runs of homozygosity represented as the number of ROH segments on the y axis and fraction of the genome contained in ROH (Mbp) on the x axis.
(D) Histogram showing the distribution of ROH segments of different size categories. The Sicilian wolves (Sic1 and Sic2) show a high number of short ROHs.
(E) Genetic load represented as the number of transversion sites that are homozygous is shown on the y axis compared to the proportion of the genome in ROH (FROH). The Sicilian wolves display a higher transversion load compared to other wolf populations.