Figure 1.
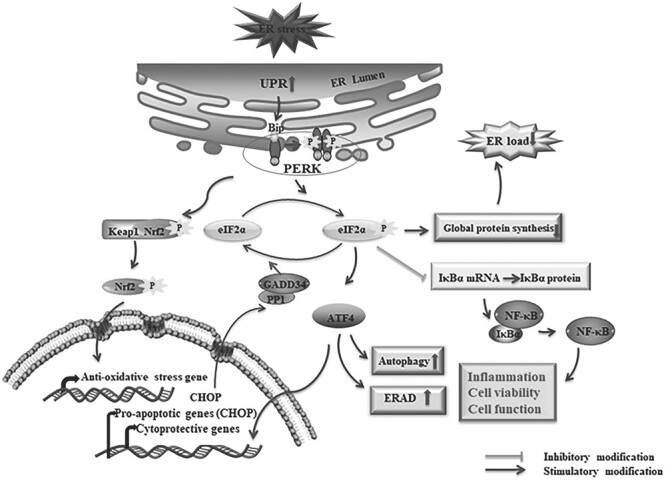
The activation of the PERK signaling pathway under ER stress. The accumulation of miss/unfolded proteins leads to activation of the PERK pathway through dissociations of BiP from the ER stress transducer. The resulting dissociations facilitate the oligomerization and autophosphorylation of PERK which further phosphorylates the eIF2α. The p-eIF2α decreases the ER load by inhibiting the global protein synthesis and induces the preferential translation of ATF4. Depending on the severity of ER stress, ATF4 induces either cytoprotective genes for cell survival or pro-apoptotic genes for apoptotic cell death as well as autophagy and ERAD-related genes. CHOP is a such kind of pro-apoptotic gene product by ATF4 induction that upregulates the GADD34 to form the complex with protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) and dephosphorylates eIF2α through the complex. In addition, the inhibition of p-eIF2α to the IκBα mRNA translation leads to dissociation of NF-κB, which mediates the transcription of several genes and induces cell functions including inflammation and cell survivability. PERK mediated phosphorylation of Nrf2, which dissociates the conjugation of Nrf2-Keap-1, resulting in accumulation and translocation of Nrf2 to the nucleus, and binds to the anti-oxidative stress gene. ‘↑’: increase; ‘↓’: decrease.
