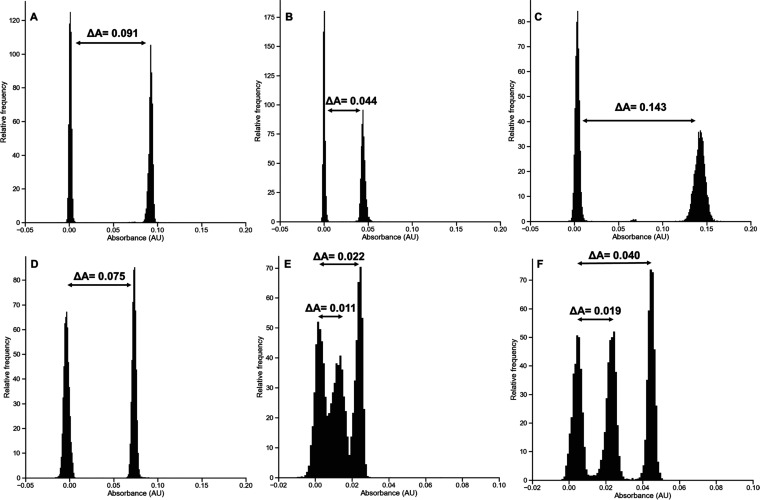
Figure 4.
Development of NADH-based coupled assays in droplets for the detection of CAZyme activity on natural substrates. As coupling enzymes were added in excess, signal differences reflect CAZymes’ intrinsic specific activities. Two control populations of droplets of identical size containing either the substrate alone in buffer (AldoUronic acids (A), wheat arabinoxylan (B), or beechwood xylan (C, D)) or supplemented with GH67 glucuronidase (A), GH51 Arafase (B), GH10 xylanase + GH43 β-xylosidase (C), or GH10 xylanase alone (D) were generated using the double flow-focussing droplet generator shown in Supporting Figure S4A. Three control droplet populations containing either CMC alone in buffer, supplemented with GH5 endo-cellulase, or supplemented with GH endo-cellulase + GH1 β-glucosidase (E), wheat arabinoxylan alone in buffer, supplemented with GH10 xylanase alone, or with GH10 xylanase + GH43 β-xylosidase (F) were generated using the droplet generator shown in Supporting Figure S3B. The droplets were further picoinjected with uronate dehydrogenase (A), galactose dehydrogenase (B), xylose dehydrogenase (C, D, F), or glucokinase + G6PDH (E) together with the appropriate cofactors, mPMS and WST-1 using the picoinjector shown in Supporting Figure S4D. After a 1 h incubation at 37 °C (A–D, F) or 25 °C (E), the droplet absorbance was measured using the sorter shown in Supporting Figure S4E.