Figure 3.
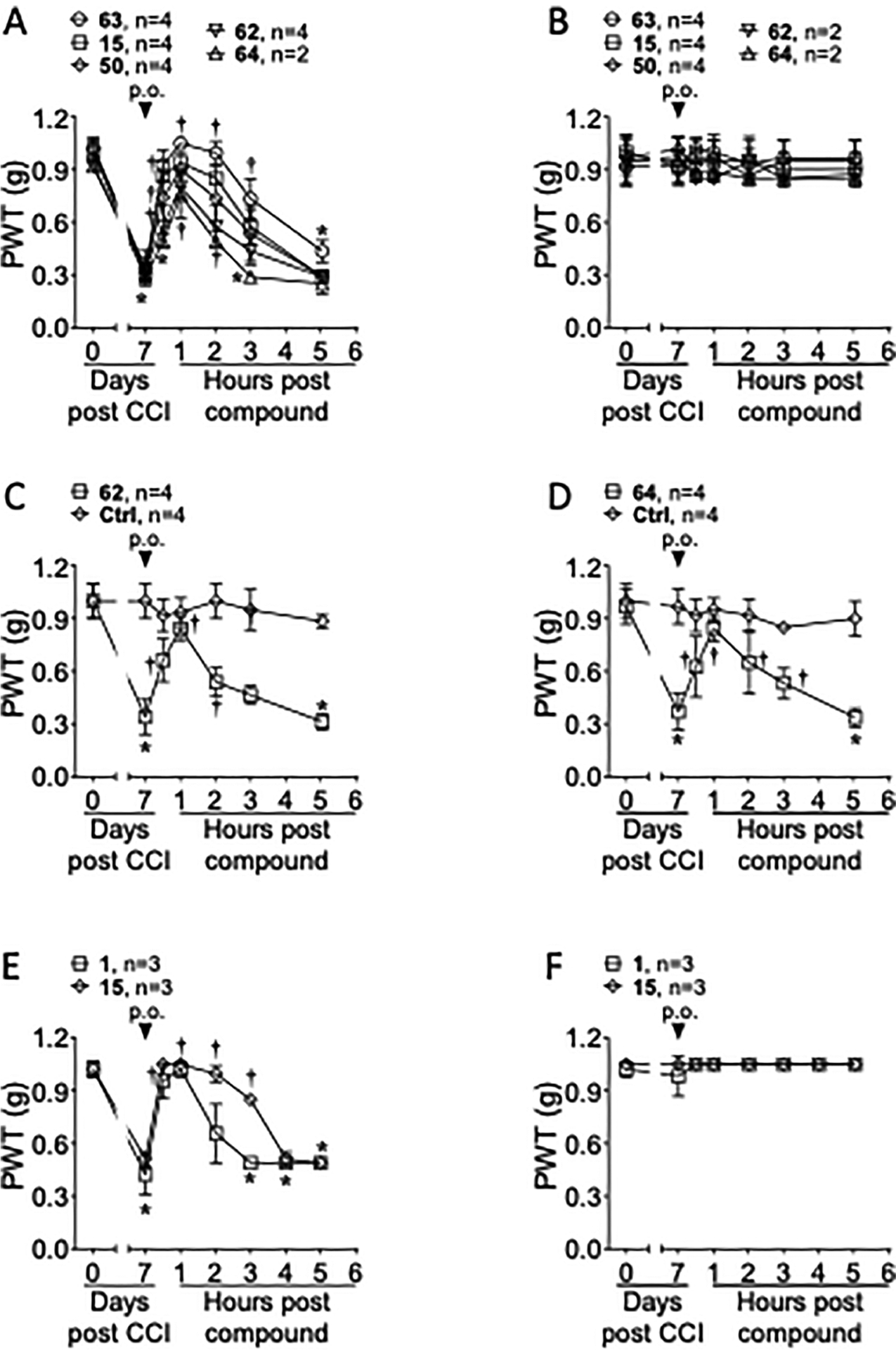
Representative time and dose dependence for reversal of established neuropathic pain in adult male mice by five newly synthesized P2Y14R antagonists and reference compound 1. The drugs were injected 7 days post-sciatic nerve constriction. The paw withdrawal threshold (PWT) was determined using von Frey filaments applied to the postsurgical hindpaw.41 (A–D) Single injection (10 μmol/kg, p.o.) of a P2Y14 R antagonist (active drug 15 or prodrugs 50 and 62–64) reversed the mechano-allodynia on the ipsilateral, nerve-injured hindpaw. (E, F) Reference antagonist 1 was compared to the potent antagonist 15, with both administered by oral gavage. A single p.o. administration (10 μmol/kg) of 1 or 15 reversed the mechano-allodynia. For all experiments, the drug injection had no effect on the contralateral hindpaw (B, F). Data were analyzed by twoway analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s comparisons, *P <0.05 versus day 0 and †P < 0.05 versus day 7. Data represent the mean ± SD. The vehicle used for the oral dosing consisted of 5% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) + 10% (5% Kolliphor HS 15:DMSO, 5:95 by volume) in 0.5% methyl cellulose (0.2 mL dose). The vehicle used for the i.p. injection: 10% (5% Kolliphor HS 15:DMSO, 5:95 by volume) in saline (0.2 mL dose). Results with other antagonists (11, 15, and 16; i.p.) in the mouse CCI model are shown in Figure S8 (Supporting Information).
