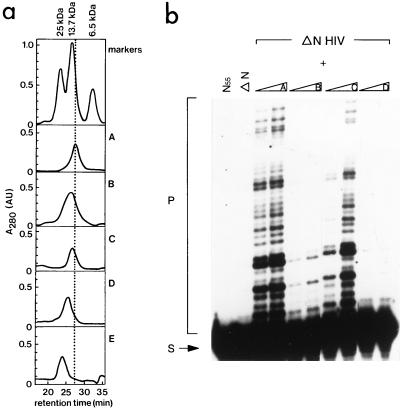
FIG. 3.
(a) Size exclusion chromatography of mutant proteins of the N-terminal domain of HIV-2 IN (amino acids 1 to 55). Proteins were injected on a Superdex 75 HR 10/30 column (Pharmacia), which had been equilibrated in buffer G (150 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 6.7], 3 mM β-mercaptoethanol, 4 μM ZnCl2). The following markers were used: aprotinin (6.5 kDa, 100 μg), RNase A (13.7 kDa, 125 μg), and chymotrypsinogen (25 kDa, 55 μg). Elution profiles are of the following proteins: wild-type IN55 (profile A), mutant F1E;L2D;I5A (profile B), mutant F1E (profile C), and mutant H12L (profile D). Profile E is of the mutant F1E in IN1–55 in the presence of 4 mM EDTA. All proteins were injected at a concentration of 0.4 mM. The retention time in minutes is indicated on the X axis, and the absorption at 280 nm (A280, in arbitrary units) is shown in the Y axis. (b) Complementation between the N-terminal deletion mutant of HIV-2 IN (ΔN HIV) and several mutants of the N-terminal domain of HIV-2 IN (IN55). In the first and second lanes, only IN55 or ΔN is present in the reaction. The N-terminal deletion mutant was incubated with the mutants of profiles A to D of IN55 (see description for panel a), prior to the integration reaction. In each two-lane panel, increasing amounts of IN55 protein were added (20 and 200 pmol, respectively). The migration positions of the substrate (S) and strand transfer products (P) are indicated on the left.