Figure 3.
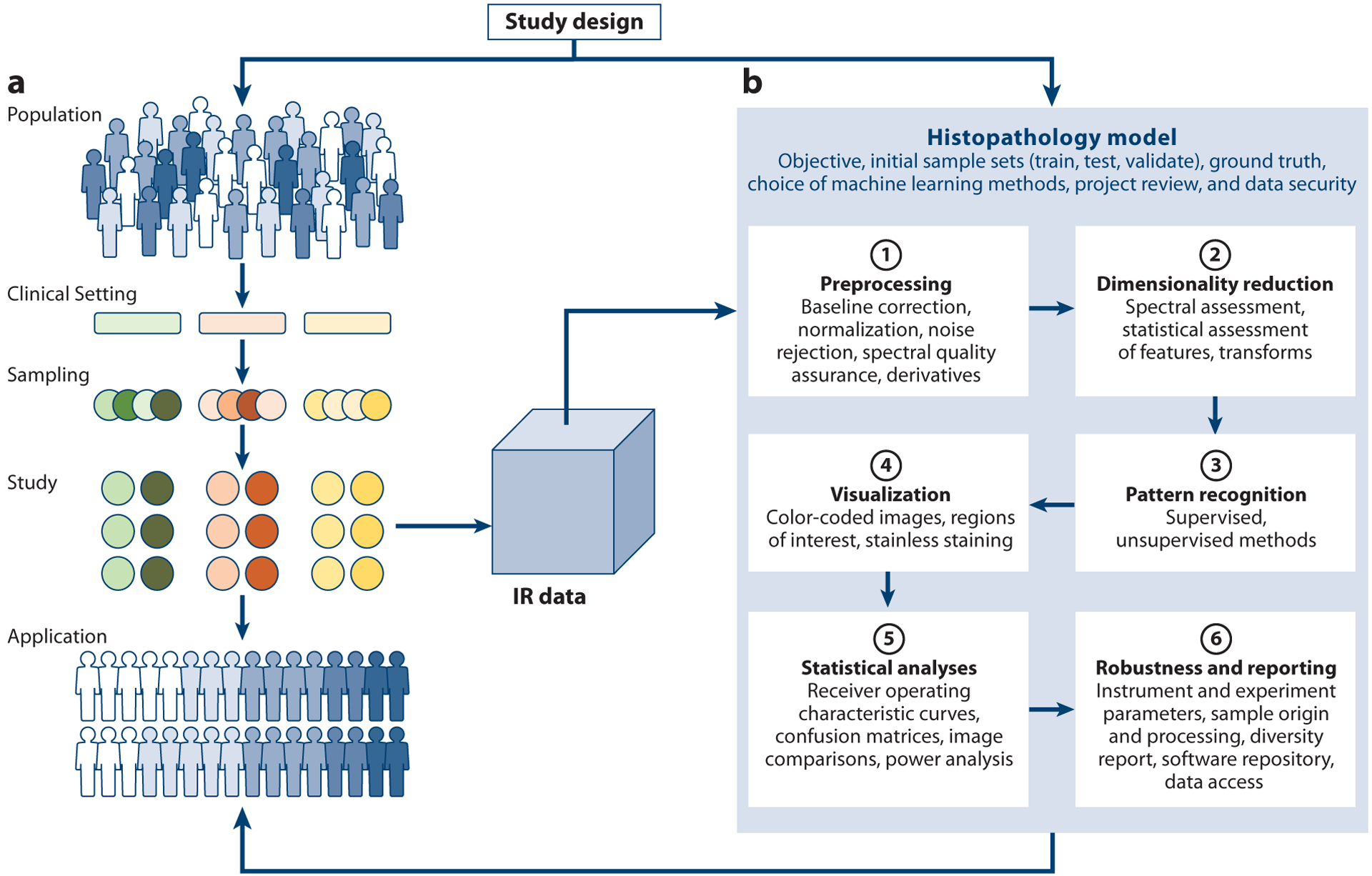
Study design and data workflows in infrared (IR)-based pathology. (a) General idea of a study design. A population of specific disease states is identified from several clinical systems for the study to assure a diversity of patients and practices. Representative cases for IR imaging are identified and tissue samples are prepared, often building in sampling redundancy (i.e., sampling from the same patients), use of matched cases (from the same patient or matching for known variables), and high statistical numbers. From each sample used in the study, an IR imaging data set is obtained. (b) A computational pipeline is then devised to assess the use of a histopathology model along with analytical parameters to process the data and extract information, with statistical validation. Multistep processing workflows are designed for specific cases as needed and benefit from the opportunity to include substantial spectroscopy and pathology knowledge. Colors of the population indicate the natural variation as well as variation due to disease, while variation introduced by clinical settings and sampling is indicated by additional colors.
