Fig. 2.
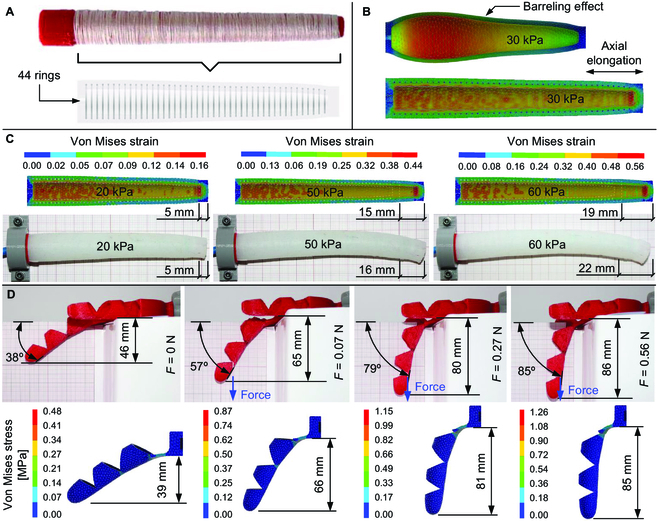
Numerical modeling and simulation of soft actuator and exoskeleton. (A) The PET reinforcement around the mold’s core is in the top image, while the bottom image shows a simplified model with a cylindrical cross-section measuring 0.25 mm in diameter and consisting of 44 rings. (B) Effect of the PET reinforcement on the elimination of the barreling effect. (C) Comparison between experimental and numerical (Ogden set3) elongation of the actuator for 3 values of applied pressure. (D) Comparison between experimental and numerical (MR set3) bending of the exoskeleton finger subject to the gravity effect and force applied at the distal joint. The maximum stress value at the proximal joint falls within the material limits. When there is no external force applied, the exoskeleton weight causes vertical displacement.
